Page 458 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 458
434 19 Chemoenzymatic Multistep One-Pot Processes
′
trimethyl aluminum and 2,2 -biphenol or even the more preferred binol. Compara-
ble results were obtained when using binol in racemic form and as enantiomerically
′
pure (R)-binol (1,1 -bi-2-naphthol), respectively. A selected example based on the
use of the latter is given in Scheme 19.8. As a biocatalyst, the lipase CAL-B was also
applied for these chemoenzymatic DKRs, which led to the formation of the resulting
esters with both high conversion and enantioselectivity. A representative example
is the transformation of racemic 1-phenyl-1-ethanol (rac-7) into its corresponding
acetate (R)-10 in a yield of 93% and with an enantioselectivity of 95% ee [24].
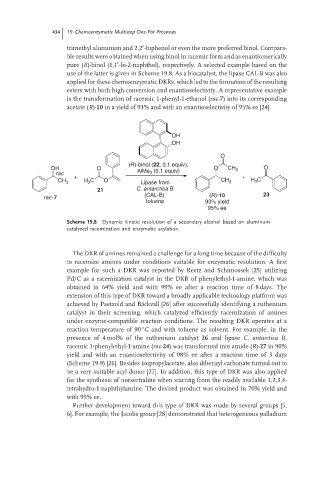
OH
OH
O
(R)-binol (22, 0.1 equiv),
OH O O CH 3 O
3
rac AlMe (0.1 equiv)
+ +
CH 3 H C O Lipase from CH 3 H C
3
3
21 C. antarctica B
(CAL-B), (R)-10 23
rac-7
toluene 93% yield
95% ee
Scheme 19.8 Dynamic kinetic resolution of a secondary alcohol based on aluminum-
catalyzed racemization and enzymatic acylation.
The DKR of amines remained a challenge for a long time because of the difficulty
to racemize amines under conditions suitable for enzymatic resolution. A first
example for such a DKR was reported by Reetz and Schimossek [25] utilizing
Pd/C as a racemization catalyst in the DKR of phenylethyl-1-amine, which was
obtained in 64% yield and with 99% ee after a reaction time of 8 days. The
extension of this type of DKR toward a broadly applicable technology platform was
achieved by Paetzold and B¨ ackvall [26] after successfully identifying a ruthenium
catalyst in their screening, which catalyzed efficiently racemization of amines
under enzyme-compatible reaction conditions. The resulting DKR operates at a
◦
reaction temperature of 90 C and with toluene as solvent. For example, in the
presence of 4 mol% of the ruthenium catalyst 26 and lipase C. antarctica B,
racemic 1-phenylethyl-1-amine (rac-24) was transformed into amide (R)-27 in 90%
yield and with an enantioselectivity of 98% ee after a reaction time of 3 days
(Scheme 19.9) [26]. Besides isopropylacetate, also dibenzyl carbonate turned out to
be a very suitable acyl donor [27]. In addition, this type of DKR was also applied
for the synthesis of norsertraline when starting from the readily available 1,2,3,4-
tetrahydro-1-naphthylamine. The desired product was obtained in 70% yield and
with 99% ee.
Further development toward this type of DKR was made by several groups [5,
6]. For example, the Jacobs group [28] demonstrated that heterogeneous palladium