Page 459 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 459
19.3 Combination of Substrate Isomerization and their Derivatization 435
Racemization
catalyst:
R O O R
H
Ph Ph
R R
R H R
Ru Ru
OC CO O
CO CO
NH 2 O CH 3 (26, 4 mol%, HN CH 3 OH
H ),
rac R = p-MeO-C 6 4 +
+ H 3 C O CH 3 H 3 C CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
Na CO , toluene, 90 °C 28
3
2
rac-24 25 Resolution catalyst: (R)-27
lipase from 90% yield
C. antarctica B (CAL-B) 98% ee
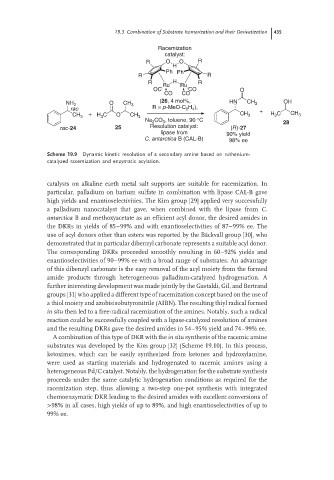
Scheme 19.9 Dynamic kinetic resolution of a secondary amine based on ruthenium-
catalyzed racemization and enzymatic acylation.
catalysts on alkaline earth metal salt supports are suitable for racemization. In
particular, palladium on barium sulfate in combination with lipase CAL-B gave
high yields and enantioselectivities. The Kim group [29] applied very successfully
a palladium nanocatalyst that gave, when combined with the lipase from C.
antarctica B and methoxyacetate as an efficient acyl donor, the desired amides in
the DKRs in yields of 85–99% and with enantioselectivities of 87–99% ee. The
use of acyl donors other than esters was reported by the B¨ ackvall group [30], who
demonstrated that in particular dibenzyl carbonate represents a suitable acyl donor.
The corresponding DKRs proceeded smoothly resulting in 60–92% yields and
enantioselectivities of 90–99% ee with a broad range of substrates. An advantage
of this dibenzyl carbonate is the easy removal of the acyl moiety from the formed
amide products through heterogeneous palladium-catalyzed hydrogenation. A
further interesting development was made jointly by the Gastaldi, Gil, and Bertrand
groups [31] who applied a different type of racemization concept based on the use of
a thiol moiety and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). The resulting thiyl radical formed
in situ then led to a free-radical racemization of the amines. Notably, such a radical
reaction could be successfully coupled with a lipase-catalyzed resolution of amines
and the resulting DKRs gave the desired amides in 54–95% yield and 74–99% ee.
A combination of this type of DKR with the in situ synthesis of the racemic amine
substrates was developed by the Kim group [32] (Scheme 19.10). In this process,
ketoximes, which can be easily synthesized from ketones and hydroxylamine,
were used as starting materials and hydrogenated to racemic amines using a
heterogeneous Pd/C catalyst. Notably, the hydrogenation for the substrate synthesis
proceeds under the same catalytic hydrogenation conditions as required for the
racemization step, thus allowing a two-step one-pot synthesis with integrated
chemoenzymatic DKR leading to the desired amides with excellent conversions of
>98% in all cases, high yields of up to 89%, and high enantioselectivities of up to
99% ee.