Page 134 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 134
112 5 Crystallization of Poly(lactic acid)
′
that the α -crystals have conformational disorder of the C –C dihedral angle.
α
The two crystalline forms present similar infrared and Raman features, the most
significant difference consists in the lowering in the frequency of the 200 cm −1
band. The frequency shift of the 200 cm −1 band is linked to a variation of the
∘
C –C trans dihedral angle, as it changes from 168.8 to 180 , evidenced by
α
simulated Raman spectra. On the basis of the combination of experimental and
simulation data, it was concluded that distortion of the chain conformation in
′
the α -structure is not localized, but distributed throughout the chain [42].
′
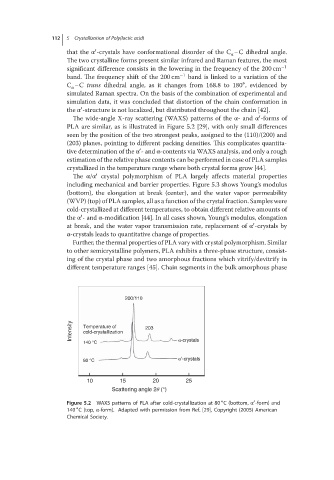
The wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) patterns of the α-and α -forms of
PLA are similar, as is illustrated in Figure 5.2 [29], with only small differences
seen by the position of the two strongest peaks, assigned to the (110)/(200) and
(203) planes, pointing to different packing densities. This complicates quantita-
′
tive determination of the α -and α-contents via WAXS analysis, and only a rough
estimation of the relative phase contents can be performed in case of PLA samples
crystallized in the temperature range where both crystal forms grow [44].
′
The α/α crystal polymorphism of PLA largely affects material properties
including mechanical and barrier properties. Figure 5.3 shows Young’s modulus
(bottom), the elongation at break (center), and the water vapor permeability
(WVP) (top) of PLA samples, all as a function of the crystal fraction. Samples were
cold-crystallized at different temperatures, to obtain different relative amounts of
′
the α -and α-modification [44]. In all cases shown, Young’s modulus, elongation
′
at break, and the water vapor transmission rate, replacement of α -crystals by
α-crystals leads to quantitative change of properties.
Further, the thermal properties of PLA vary with crystal polymorphism. Similar
to other semicrystalline polymers, PLA exhibits a three-phase structure, consist-
ing of the crystal phase and two amorphous fractions which vitrify/devitrify in
different temperature ranges [45]. Chain segments in the bulk amorphous phase
200/110
Intensity Temperature of 203
cold-crystallization
140 °C α-crystals
80 °C α′-crystals
10 15 20 25
Scattering angle 2θ (°)
∘
′
Figure 5.2 WAXS patterns of PLA after cold-crystallization at 80 C(bottom, α -form) and
∘
140 C(top, α-form). Adapted with permission from Ref. [29], Copyright (2005) American
Chemical Society.