Page 72 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 72
50 3 Microbial Synthesis of Biodegradable Polyesters: Processes, Products, Applications
O O
− −
HO O HO O
5-Hydroxyhexanoate 3-Hydroxybutyrate
O O O O
− − − HO −
HO O HO O HO O O O
3-Hydroxy-2- 3-Hydroxy-4-trans- 3-Hydroxy-2-butenoate 4-Hydroxybutyrate
methylbutyrate hexenoate
O
NO 2
−
HO O
3-Hydroxy-6,7-
N CI epoxydodecanoate
O
O
O O O O O O
− − − − − −
HO O HO O HO O HO O HO O HO O
para-Nitrophenoxy Phenoxy- 7-Cyano- 3-Hydroxy- 3-Hydroxy- 3-Hydroxyhexadecanoate
3-hydroxyhexanoate 3-hydroxybutyrate 3-hydroxyheptanoate 4-methylnonanoate 8-chlorooctanoate
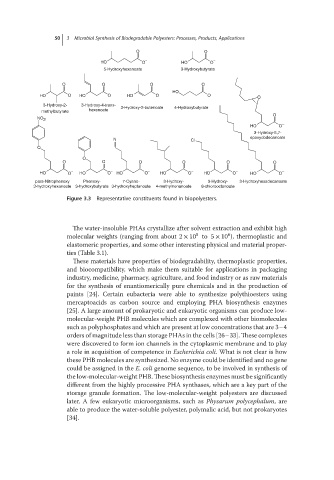
Figure 3.3 Representative constituents found in biopolyesters.
The water-insoluble PHAs crystallize after solvent extraction and exhibit high
6
5
molecular weights (ranging from about 2 × 10 to 5 × 10 ), thermoplastic and
elastomeric properties, and some other interesting physical and material proper-
ties (Table 3.1).
These materials have properties of biodegradability, thermoplastic properties,
and biocompatibility, which make them suitable for applications in packaging
industry, medicine, pharmacy, agriculture, and food industry or as raw materials
for the synthesis of enantiomerically pure chemicals and in the production of
paints [24]. Certain eubacteria were able to synthesize polythioesters using
mercaptoacids as carbon source and employing PHA biosynthesis enzymes
[25]. A large amount of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms can produce low-
molecular-weight PHB molecules which are complexed with other biomolecules
such as polyphosphates and which are present at low concentrations that are 3–4
orders of magnitude less than storage PHAs in the cells [26–33]. These complexes
were discovered to form ion channels in the cytoplasmic membrane and to play
a role in acquisition of competence in Escherichia coli.Whatisnot clearishow
these PHB molecules are synthesized. No enzyme could be identified and no gene
could be assigned in the E. coli genome sequence, to be involved in synthesis of
the low-molecular-weight PHB. These biosynthesis enzymes must be significantly
different from the highly processive PHA synthases, which are a key part of the
storage granule formation. The low-molecular-weight polyesters are discussed
later. A few eukaryotic microorganisms, such as Physarum polycephalum,are
able to produce the water-soluble polyester, polymalic acid, but not prokaryotes
[34].