Page 211 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 211
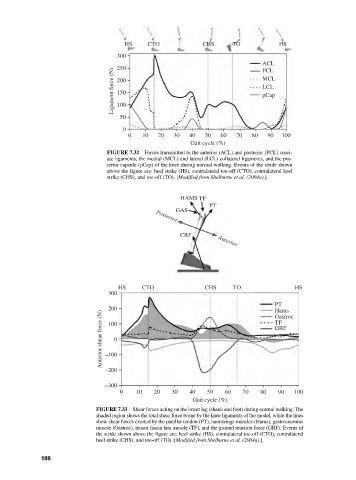
HS CTO CHS TO HS
300
ACL
250
Ligament force (N) 200 MCL
PCL
LCL
150
pCap
100
50
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Gait cycle (%)
FIGURE 7.32 Forces transmitted to the anterior (ACL) and posterior (PCL) cruci-
ate ligaments, the medial (MCL) and lateral (LCL) collateral ligaments, and the pos-
terior capsule (pCap) of the knee during normal walking. Events of the stride shown
above the figure are: heel strike (HS), contralateral toe-off (CTO), contralateral heel
strike (CHS), and toe-off (TO). [Modified from Shelburne et al. (2004a).]
HAMS TF
PT
GAS
Posterior
CRF Anterior
HS CTO CHS TO HS
300
PT
200 Hams
Anterior shear force (N) –100 GRF
Gastroc
TF
100
0
–200
–300
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Gait cycle (%)
FIGURE 7.33 Shear forces acting on the lower leg (shank and foot) during normal walking. The
shaded region shows the total shear force borne by the knee ligaments of the model, while the lines
show shear forces exerted by the patellar tendon (PT), hamstrings muscles (Hams), gastrocnemius
muscle (Gastroc), tensor fascia lata muscle (TF), and the ground reaction force (GRF). Events of
the stride shown above the figure are: heel strike (HS), contralateral toe-off (CTO), contralateral
heel strike (CHS), and toe-off (TO). [Modified from Shelburne et al. (2004a).]
188