Page 317 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 2, Applications
P. 317
THE PRINCIPLES OF X-RAY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 295
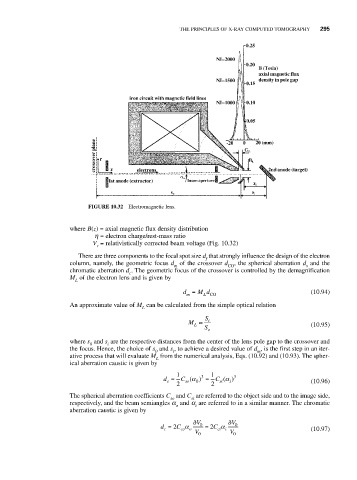
FIGURE 10.32 Electromagnetic lens.
where B(z) = axial magnetic flux density distribution
h = electron charge/rest-mass ratio
V = relativistically corrected beam voltage (Fig. 10.32)
r
There are three components to the focal spot size d that strongly influence the design of the electron
f
column, namely, the geometric focus d of the crossover d , the spherical aberration d and the
m CO s
chromatic aberration d . The geometric focus of the crossover is controlled by the demagnification
c
M of the electron lens and is given by
L
d = M d (10.94)
m
L CO
An approximate value of M can be calculated from the simple optical relation
L
S
M ≈ i (10.95)
L
S o
where s and s are the respective distances from the center of the lens pole gap to the crossover and
0 i
the focus. Hence, the choice of s and s , to achieve a desired value of d , is the first step in an iter-
0 i m
ative process that will evaluate M from the numerical analysis, Eqs. (10.92) and (10.93). The spher-
L
ical aberration caustic is given by
1 3 1 3
α
d = C (α 0 ) = C ( ) (10.96)
s
si
i
so
2 2
The spherical aberration coefficients C and C are referred to the object side and to the image side,
so si
respectively, and the beam semiangles a and a are referred to in a similar manner. The chromatic
o i
aberration caustic is given by
δ V δ V
d = 2 C α 0 = 2 C α 0 (10.97)
ci i
co o
c
V 0 V 0