Page 177 - Boiler_Operators_Handbook,_Second_Edition
P. 177
162 Boiler Operator’s Handbook
tubes of the condensers were made of
high-quality brass and bronze. Sacri-
ficial magnesium anodes electrically
connected to the condensers provided
additional protection against corrosion.
Plants using seawater or brackish water
would be constructed similarly but, if
large, use electrically powered cathodic
protection for corrosion. Growth of al-
gae, bacteria, bivalves, etc., on the heat
transfer surfaces are also concerns for
those condensers. The pressure drop
through and temperature differential of
these condensers has to be monitored
closely to identify conditions of organic
growth hindering heat transfer.
Well water will have the highest
dissolved solids content of any supply
Figure 5-16. Evaporative condenser
of condenser cooling water. Normally,
when the well water is not circulated,
it will not present a problem. However, I have seen
sources that will form scale on heat transfer surfaces
after a temperature rise of only a few degrees. Regu-
lar sampling and testing of the TDS of the well water
should allow you to detect conditions that could con-
tribute to scaling. The important thing to do with high
solids water is to maintain a minimum rate of water
flow through the condenser and avoid concentrating
solids content by blowdown or other means.
Water drawn from rivers, lakes and reservoirs will
normally have lower dissolved solids content but can
have a considerably higher organic materials content.
Water circulating through a condenser and the cooling
tower will also pick up organic materials. When those
waters are used in condensers they will require regular
cleanings to remove the organics, algae, and bacterial
growth. Monitoring of the pressure and temperature
differentials under these conditions is imperative.
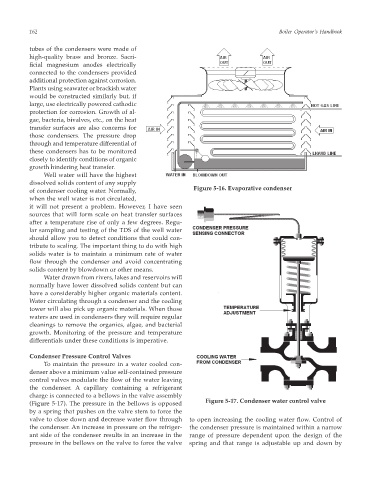
Condenser Pressure Control Valves
To maintain the pressure in a water cooled con-
denser above a minimum value self-contained pressure
control valves modulate the flow of the water leaving
the condenser. A capillary containing a refrigerant
charge is connected to a bellows in the valve assembly
Figure 5-17. Condenser water control valve
(Figure 5-17). The pressure in the bellows is opposed
by a spring that pushes on the valve stem to force the
valve to close down and decrease water flow through to open increasing the cooling water flow. Control of
the condenser. An increase in pressure on the refriger- the condenser pressure is maintained within a narrow
ant side of the condenser results in an increase in the range of pressure dependent upon the design of the
pressure in the bellows on the valve to force the valve spring and that range is adjustable up and down by