Page 115 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 115
100 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
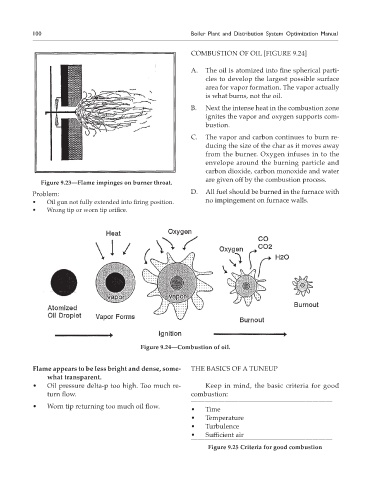
COMBUSTION OF OIL [FIGURE 9.24]
A. The oil is atomized into fine spherical parti-
cles to develop the largest possible surface
area for vapor formation. The vapor actually
is what burns, not the oil.
B. Next the intense heat in the combustion zone
ignites the vapor and oxygen supports com-
bustion.
C. The vapor and carbon continues to burn re-
ducing the size of the char as it moves away
from the burner. Oxygen infuses in to the
envelope around the burning particle and
carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and water
are given off by the combustion process.
Figure 9.23—Flame impinges on burner throat.
Problem: D. All fuel should be burned in the furnace with
• Oil gun not fully extended into firing position. no impingement on furnace walls.
• Wrong tip or worn tip orifice.
Figure 9.24—Combustion of oil.
Flame appears to be less bright and dense, some- THE BASICS OF A TUNEUP
what transparent.
• Oil pressure delta-p too high. Too much re- Keep in mind, the basic criteria for good
turn flow. combustion:
—————————————————————
• Worn tip returning too much oil flow.
• Time
• Temperature
• Turbulence
• Sufficient air
—————————————————————
Figure 9.25 Criteria for good combustion