Page 272 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 272
Steam Traps 257
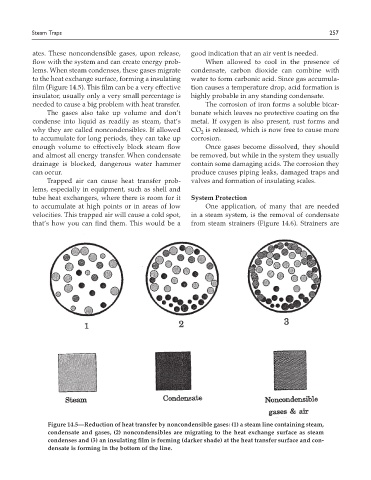
ates. These noncondensible gases, upon release, good indication that an air vent is needed.
flow with the system and can create energy prob- When allowed to cool in the presence of
lems. When steam condenses, these gases migrate condensate, carbon dioxide can combine with
to the heat exchange surface, forming a insulating water to form carbonic acid. Since gas accumula-
film (Figure 14.5). This film can be a very effective tion causes a temperature drop, acid formation is
insulator, usually only a very small percentage is highly probable in any standing condensate.
needed to cause a big problem with heat transfer. The corrosion of iron forms a soluble bicar-
The gases also take up volume and don’t bonate which leaves no protective coating on the
condense into liquid as readily as steam, that’s metal. If oxygen is also present, rust forms and
why they are called noncondensibles. If allowed CO is released, which is now free to cause more
2
to accumulate for long periods, they can take up corrosion.
enough volume to effectively block steam flow Once gases become dissolved, they should
and almost all energy transfer. When condensate be removed, but while in the system they usually
drainage is blocked, dangerous water hammer contain some damaging acids. The corrosion they
can occur. produce causes piping leaks, damaged traps and
Trapped air can cause heat transfer prob- valves and formation of insulating scales.
lems, especially in equipment, such as shell and
tube heat exchangers, where there is room for it System Protection
to accumulate at high points or in areas of low One application, of many that are needed
velocities. This trapped air will cause a cold spot, in a steam system, is the removal of condensate
that’s how you can find them. This would be a from steam strainers (Figure 14.6). Strainers are
Figure 14.5—Reduction of heat transfer by noncondensible gases: (1) a steam line containing steam,
condensate and gases, (2) noncondensibles are migrating to the heat exchange surface as steam
condenses and (3) an insulating film is forming (darker shade) at the heat transfer surface and con-
densate is forming in the bottom of the line.