Page 275 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 275
260 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
Figure 14.8—Water steam density relationship.
Inverted Bucket Traps
Inverted bucket traps use an open inverted
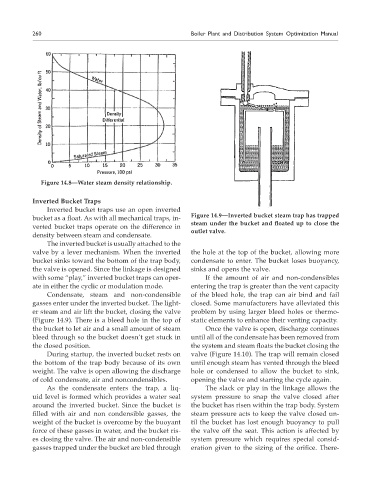
Figure 14.9—Inverted bucket steam trap has trapped
bucket as a float. As with all mechanical traps, in-
steam under the bucket and floated up to close the
verted bucket traps operate on the difference in
outlet valve.
density between steam and condensate.
The inverted bucket is usually attached to the
valve by a lever mechanism. When the inverted the hole at the top of the bucket, allowing more
bucket sinks toward the bottom of the trap body, condensate to enter. The bucket loses buoyancy,
the valve is opened. Since the linkage is designed sinks and opens the valve.
with some “play,” inverted bucket traps can oper- If the amount of air and non-condensibles
ate in either the cyclic or modulation mode. entering the trap is greater than the vent capacity
Condensate, steam and non-condensible of the bleed hole, the trap can air bind and fail
gasses enter under the inverted bucket. The light- closed. Some manufacturers have alleviated this
er steam and air lift the bucket, closing the valve problem by using larger bleed holes or thermo-
(Figure 14.9). There is a bleed hole in the top of static elements to enhance their venting capacity.
the bucket to let air and a small amount of steam Once the valve is open, discharge continues
bleed through so the bucket doesn’t get stuck in until all of the condensate has been removed from
the closed position. the system and steam floats the bucket closing the
During startup, the inverted bucket rests on valve (Figure 14.10). The trap will remain closed
the bottom of the trap body because of its own until enough steam has vented through the bleed
weight. The valve is open allowing the discharge hole or condensed to allow the bucket to sink,
of cold condensate, air and non condensibles. opening the valve and starting the cycle again.
As the condensate enters the trap, a liq- The slack or play in the linkage allows the
uid level is formed which provides a water seal system pressure to snap the valve closed after
around the inverted bucket. Since the bucket is the bucket has risen within the trap body. System
filled with air and non condensible gasses, the steam pressure acts to keep the valve closed un-
weight of the bucket is overcome by the buoyant til the bucket has lost enough buoyancy to pull
force of these gasses in water, and the bucket ris- the valve off the seat. This action is affected by
es closing the valve. The air and non-condensible system pressure which requires special consid-
gasses trapped under the bucket are bled through eration given to the sizing of the orifice. There-