Page 170 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 170
Polycondensation Polymers 133
Aliphatic polyketones are made from the reaction of olefin monomers and carbon monoxide
using a variety of catalysts. Shell commercialized a terpolymer of carbon monoxide, ethylene, and
a small amount of propylene in 1996 under the trade name of Carilon (Equation 4.86). They have a
o
o
useful range between the T (15 C) and T (200 C) that corresponds to the general useful range of
g m
use temperatures for most industrial applications. The presence of polar groups causes the materials
to be tough with the starting materials readily available.
H C O CH
2
+ + CO 3
H C CH 2
2
CH 3 R
R (4.86)
O
Aromatic polyketone
4.15 PHENOLIC AND AMINO PLASTICS
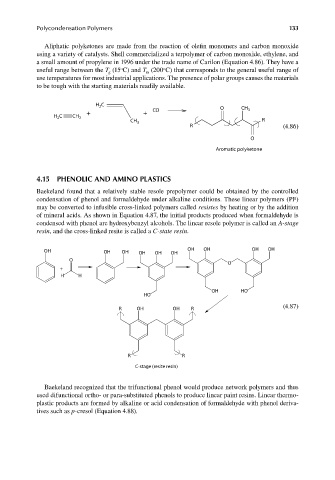
Baekeland found that a relatively stable resole prepolymer could be obtained by the controlled
condensation of phenol and formaldehyde under alkaline conditions. These linear polymers (PF)
may be converted to infusible cross-linked polymers called resistes by heating or by the addition
of mineral acids. As shown in Equation 4.87, the initial products produced when formaldehyde is
condensed with phenol are hydroxybenzyl alcohols. The linear resole polymer is called an A-stage
resin, and the cross-linked resite is called a C-state resin.
OH OH OH OH OH OH OH OH OH OH
O
O
+
H H
OH HO
HO
(4.87)
R OH OH R
R R
C-stage (resite resin)
Baekeland recognized that the trifunctional phenol would produce network polymers and thus
used difunctional ortho- or para-substituted phenols to produce linear paint resins. Linear thermo-
plastic products are formed by alkaline or acid condensation of formaldehyde with phenol deriva-
tives such as p-cresol (Equation 4.88).
9/14/2010 3:38:35 PM
K10478.indb 133
K10478.indb 133 9/14/2010 3:38:35 PM