Page 173 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 173
160 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
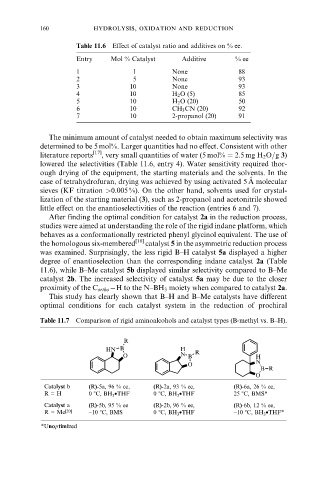
Table 11.6 Effect of catalyst ratio and additives on % ee.
Entry Mol % Catalyst Additive % ee
1 1 None 88
2 5 None 93
3 10 None 93
4 10 H 2 O (5) 85
5 10 H 2 O (20) 50
6 10 CH 3 CN (20) 92
7 10 2-propanol (20) 91
The minimum amount of catalyst needed to obtain maximum selectivity was
determined to be 5 mol%. Larger quantities had no effect. Consistent with other
literature reports [17] , very small quantities of water (5 mol% 2.5 mg H 2 O=g 3)
lowered the selectivities (Table 11.6, entry 4). Water sensitivity required thor-
ough drying of the equipment, the starting materials and the solvents. In the
Ê
case of tetrahydrofuran, drying was achieved by using activated 5 A molecular
sieves (KF titration >0.005 %). On the other hand, solvents used for crystal-
lization of the starting material (3), such as 2-propanol and acetonitrile showed
little effect on the enantioselectivities of the reaction (entries 6 and 7).
After finding the optimal condition for catalyst 2a in the reduction process,
studies were aimed at understanding the role of the rigid indane platform, which
behaves as a conformationally restricted phenyl glycinol equivalent. The use of
the homologous six-membered [18] catalyst 5 in the asymmetric reduction process
was examined. Surprisingly, the less rigid B±H catalyst 5a displayed a higher
degree of enantioselection than the corresponding indane catalyst 2a (Table
11.6), while B±Me catalyst 5b displayed similar selectivity compared to B±Me
catalyst 2b. The increased selectivity of catalyst 5a may be due to the closer
proximity of the C ortho ÿH to the N±BH 3 moiety when compared to catalyst 2a.
This study has clearly shown that B±H and B±Me catalysts have different
optimal conditions for each catalyst system in the reduction of prochiral
Table 11.7 Comparison of rigid aminoalcohols and catalyst types (B-methyl vs. B±H).
R
HN B H R
O N B H
N
O
B R
O
Catalyst b (R)-5a, 96 % ee, (R)-2a, 93 % ee, (R)-6a, 26 % ee,
R = H 0 8C, BH 3 •THF 0 8C, BH 3 •THF 25 8C, BMS*
Catalyst a (R)-5b, 95 % ee (R)-2b, 96 % ee, (R)-6b, 12 % ee,
R = Me [20] −10 8C, BMS 0 8C, BH 3 •THF −10 8C, BH 3 •THF*
*Unoptimized