Page 174 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 174
asymmetric reduction using nonmetallic catalysts 161
ketones. The highest selectivities are observed with catalyst 5a (tetralin plat-
form) and catalyst 2b, and the lowest with catalysts 6a and 6b. From a practical
point of view, B±H catalyst systems are much more preferred than B±alkyl
systems. Therefore, the use of highly effective B±H oxazaborolidine catalysts
from readily accessible tetralin and aminoindanol is recommended.
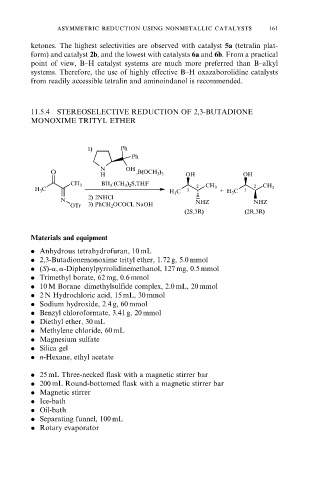
11.5.4 STEREOSELECTIVE REDUCTION OF 2,3-BUTADIONE
MONOXIME TRITYL ETHER
1) Ph
Ph
N OH
O H ,B(OCH 3 ) 3 OH OH
CH 3 BH 3 ·(CH 3 ) 2 S,THF 2 CH 3 2 CH 3
H 3 C
H 3 C 3 + H 3 C 3
2) 2NHCl
N NHZ NHZ
OTr 3) PhCH 2 OCOCl, NaOH
(2S,3R) (2R,3R)
Materials and equipment
. Anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, 10 mL
. 2,3-Butadionemonoxime trityl ether, 1.72 g, 5.0 mmol
. (S)-a, a-Diphenylpyrrolidinemethanol, 127 mg, 0.5 mmol
. Trimethyl borate, 62 mg, 0.6 mmol
. 10 M Borane±dimethylsulfide complex, 2.0 mL, 20 mmol
. 2 N Hydrochloric acid, 15 mL, 30 mmol
. Sodium hydroxide, 2.4 g, 60 mmol
. Benzyl chloroformate, 3.41 g, 20 mmol
. Diethyl ether, 30 mL
. Methylene chloride, 60 mL
. Magnesium sulfate
. Silica gel
. n-Hexane, ethyl acetate
. 25 mL Three-necked flask with a magnetic stirrer bar
. 200 mL Round-bottomed flask with a magnetic stirrer bar
. Magnetic stirrer
. Ice-bath
. Oil-bath
. Separating funnel, 100 mL
. Rotary evaporator