Page 179 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 179
166 hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction
2H), 4.02±4.18 (m, 2H), 7.10 (brd, 1H), 7.42±7.56 (m, 3H), 7.82 (d, J 6.7 Hz,
2H).
11.6 ENANTIOSELECTIVE REDUCTION OF KETONES USING N-
ARYLSULFONYL OXAZABOROLIDINES
Mukund P. Sibi, Pingrong Liu, and Gregory R. Cook
Center for Main Group Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, North Dakota State Uni-
versity, Fargo ND, 58105±5516, Sibi@plains.nodak.edu, grcook@plains.nodak.edu
11.6.1 SYNTHESIS OF N-(2-PYRIDINESULFONYL)-1-AMINO-2-
INDANOL
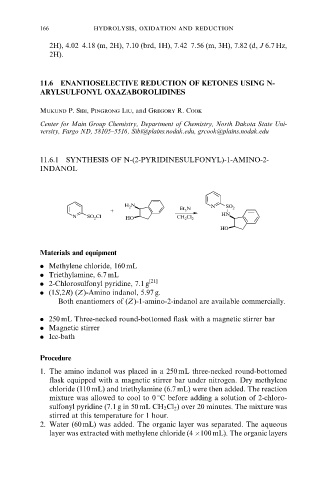
H 2 N N SO 2
+ Et 3 N
N SO 2 Cl HO CH 2 Cl 2 HN
HO
Materials and equipment
. Methylene chloride, 160 mL
. Triethylamine, 6.7 mL
. 2-Chlorosulfonyl pyridine, 7.1 g [21]
. (1S,2R) (Z)-Amino indanol, 5.97 g.
Both enantiomers of (Z)-1-amino-2-indanol are available commercially.
. 250 mL Three-necked round-bottomed flask with a magnetic stirrer bar
. Magnetic stirrer
. Ice-bath
Procedure
1. The amino indanol was placed in a 250 mL three-necked round-bottomed
flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer bar under nitrogen. Dry methylene
chloride (110 mL) and triethylamine (6.7 mL) were then added. The reaction
mixture was allowed to cool to 0 8C before adding a solution of 2-chloro-
sulfonyl pyridine (7.1 g in 50 mL CH 2 Cl 2 ) over 20 minutes. The mixture was
stirred at this temperature for 1 hour.
2. Water (60 mL) was added. The organic layer was separated. The aqueous
layer was extracted with methylene chloride (4 100 mL). The organic layers