Page 184 - Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis Vol 1 - Robert & Poignant
P. 184
asymmetric reduction using nonmetallic catalysts 171
General experimental procedure for preparation of Mosher esters [27]
For (S)-1-phenylethanol: (S)-1-phenylethanol (2 mg, 0.02 mmol) and MTPA-Cl
() (4 mL, 0.02 mmol) were mixed with carbon tetrachloride (3 drops) and dry
pyridine (3 drops). The reaction mixture was allowed to stand in a stoppered
flask for 12 hours at ambient temperature. Water (1 mL) was added and the
reaction mixture transferred to a separatory funnel and extracted with ether
(20 mL). The ether solution, after washing successively with HCl (1 M, 20 mL),
and saturated sodium carbonate solution (20 mL), and water (20 mL), was
dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and solvents were removed in vacuo. The
residue was dissolved in deuteriated chloroform for NMR analysis. The relative
integration of the hydrogen on the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group was used
to calculate the ee.
1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 200 MHz): d 1.56 (d, 3H, J 6.5 Hz, PhCH(OH)CH 3 ),
2.76 (bs, 1H, PhCH(OH)CH 3 ), 4.94 (q, 1H, J 6.5 Hz, PhCH(OH)CH 3 ), 7.32±
7.45 (m, 5H arom ).
13
C NMR (CDCl 3 , 200 MHz): d 24.97, 69.99, 125.24, 127.14, 128.24, 145.75.
ÿ1
FTIR (neat, KBr disc) n (cm ) 3364, 3065, 3031, 2974, 2929, 1728, 1603,
1494, 1452, 1371, 1287, 1204, 1077, 1030, 1011, 900, 762, 700, 607, 541.
Conclusion
The stereoselective reduction may be applied to a variety of ketones. Some
examples of reductions, as a function both of ketone substrate and amino acid
catalyst are provided in Table 11.9. The full scope of this procedure [26±28] has
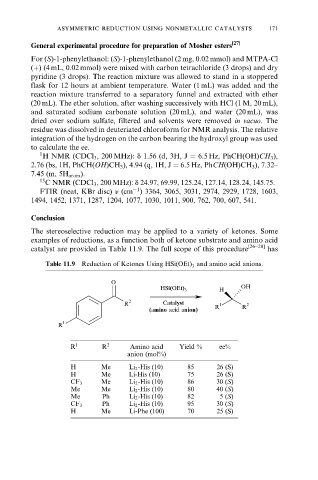
Table 11.9 Reduction of Ketones Using HSi(OEt) and amino acid anions.
3
O
HSi(OEt) 3 H OH
R 2 Catalyst 1 2
(amino acid anion) R R
R 1
R 1 R 2 Amino acid Yield % ee%
anion (mol%)
H Me Li 2 -His (10) 85 26 (S)
H Me Li-His (10) 75 26 (S)
Me Li 2 -His (10) 86 30 (S)
CF 3
Me Me Li 2 -His (10) 80 40 (S)
Me Ph Li 2 -His (10) 82 5 (S)
Ph Li 2 -His (10) 95 30 (S)
CF 3
H Me Li-Phe (100) 70 25 (S)