Page 107 - Chalcogenide Glasses for Infrared Optics
P. 107
Glass Pr oduction 85
a person who had been thoroughly trained in the Central Research
Laboratories at TI. The author had worked with him many times. The
most difficult job they worked on together was the building of a far
infrared (95.8-µm) pure He laser. The author felt Whaley was the best
person for the job and recruited him as the first employee of
Amorphous Materials. He joined the company as a stockholder and
a vice president. Whaley developed quartz fabrication techniques
that all his former colleagues from TI told him were impossible.
The task at AMI was different from the one at TI. It has been pre-
viously pointed out that AMI was not allowed to produce TI 1173 and
was forced to revert to the Ge-As-Se glass, called TI 20. The glass
was renamed Amtir 1. The fact that the glass contained arsenic—not
antimony—made it better suited for distillation. Besides, the compo-
sition had been carefully selected so that it had no tendency to form
crystallites as did the troubled TI 1173. Over a period of months, the
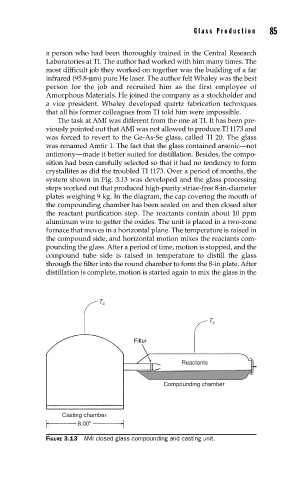
system shown in Fig. 3.13 was developed and the glass processing
steps worked out that produced high-purity striae-free 8-in-diameter
plates weighing 9 kg. In the diagram, the cap covering the mouth of
the compounding chamber has been sealed on and then closed after
the reactant purification step. The reactants contain about 10 ppm
aluminum wire to getter the oxides. The unit is placed in a two-zone
furnace that moves in a horizontal plane. The temperature is raised in
the compound side, and horizontal motion mixes the reactants com-
pounding the glass. After a period of time, motion is stopped, and the
compound tube side is raised in temperature to distill the glass
through the filter into the round chamber to form the 8-in plate. After
distillation is complete, motion is started again to mix the glass in the
T c
T c
Filter
Reactants
Compounding chamber
Casting chamber
8.00"
FIGURE 3.13 AMI closed glass compounding and casting unit.