Page 184 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 184
156 FLUID TRANSPORT EQUIPMENT
fraction weighted heat capacities of the pure components,
c, = xxicpi. (7.31)
REAL PROCESSES AND GASES
Compression in reciprocating and centrifugal compressors is
essentially adiabatic but it is not frictionless. The pressure-volume
behavior in such equipment often conforms closely to the equation
PV" = PIV; = const. (7.32)
Such a process is called polytropic. The equation is analogous to the
isentropic equation (7.20) but the polytropic exponent n is different
from the heat capacity ratio k.
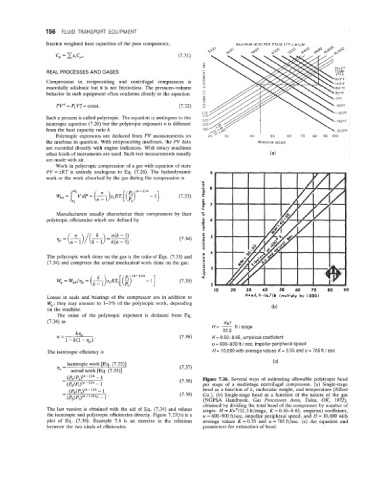
Polytropic exponents are deduced from PV measurements on 25 ' 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
the machine in question. With reciprocating machines, the PV data MOLECULAR WEIGHT
are recorded directly with engine indicators. With rotary machines
other kinds of instruments are used. Such test measurements usually (a)
are made with air.
Work in polytropic compression of a gas with equation of state
PV = zRT is entirely analogous to Eq. (7.26). The hydrodynamic
work or the work absorbed by the gas during the compression is
= (5)z1RTl[ (2)'
n-l)/n
W,, = $,dP - 11. (7.33)
Manufacturers usually characterize their compressors by their
polytropic efficiencies which are defined by
(7.34)
The polytropic work done on the gas is the ratio of Eqs. (7.33) and
(7.34) and comprises the actual mechanical work done on the gas:
(7.35)
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 00 90
Losses in seals and bearings of the compressor are in addition to Wead,lt-Ib/lb (multiply by 1000)
Wp; they may amount to 1-3% of the polytropic work, depending
on the machine. (b)
The value of the polytropic exponent is deduced from Eq.
(7.34) as Ku2
H= __ ftlstage
32.2
(7.36) K= 0.50-0.65, empirical coefficient
u = 600-900 ft I sec, impeller peripheral speed
The isentropic efficiency is H = 10,000 with average values K= 0.55 and u = 765 ft I sec
'' isentropic work [Eq. (7.25)] (7.37) (C)
=
actual work [Eq. (7.35)]
(7.38) Figure 7.26. Several ways of estimating allowable polytropic head
per stage of a multistage centrifugal compressor. (a) Single-stage
head as a function of k, molecular weight, and temperature (Elliott
(7.39) Co.). (b) Single-stage head as a function of the nature of the gas
(NGPSA Handbook, Gas Processors Assn, Tulsa, OK, 1972),
obtained by dividing the total head of the compressor by number of
The last version is obtained with the aid of Eq. (7.34) and relates stages. H = Ku2/32.2 ft/stage, K = 0.50-0.65, empirical coefficient,
the isentropic and polytropic efficiencies directly. Figure 7.27(b) is a u = 600-900 ft/sec, impeller peripheral speed, and H = 10,000 with
plot of Eq. (7.39). Example 7.6 is an exercise in the relations average values K =0.55 and u =765ft/sec. (c) An equation and
between the two kinds of efficiencies. parameters for estimation of head.