Page 188 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 188
160 FLUID TRANSPORT EQUIPMENT
EXAMPLE 7.7
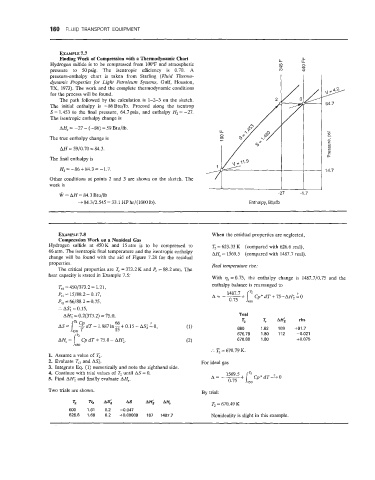
Finding Work of Compression with a Thermodynamic Chart LL LL
U
Hydrogen sulfide is to be compressed from 100°F and atmospheric m e 3
pressure to 50psig. The isentropic efficiency is 0.70. A m
pressure-enthalpy chart is taken from Starling (Fluid Thermo-
dynamic Properties for Light Petroleum System, Gulf, Houston,
TX, 1973). The work and the complete thermodynamic conditions
for the process will be found.
The path followed by the calculation is 1-2-3 on the sketch.
The initial enthalpy is -86Btu/lb. Proceed along the isentrop
S = 1.453 to the final pressure, 64.7 psia, and enthalpy H, = -27.
The isentropic enthalpy change is
AH, = -27 - (-86) = 59 Btu/lb. .-
Ln
11
The true enthalpy change is
AH = 59/0.70 = 84.3.
The final enthalpy is
H3= -86 + 84.3 = -1.7.
Other conditions at points 2 and 3 are shown on the sketch. The
work is
-27 -1.7
W = AH = 84.3 Btu/lb
+ 84.3/2.545 = 33.1 HP hr/(1000 Ib). Enthalpy, Btu/lb
EXAMPLE 7.8 When the residual properties are neglected,
Compression Work on a Nonideal Gas
Hydrogen sulfide at 450K and 15atm is to be compressed to & = 623.33 K (compared with 626.6 real),
66 atm. The isentropic final temperature and the isentropic enthalpy AH3 = 1569.5 (compared with 1487.7 real).
change will be found with the aid of Figure 7.28 for the residual
properties. Real temperature rise:
The critical properties are T, = 373.2 K and P, = 88.2 atm. The
heat capacity is stated in Example 7.5: With rl, = 0.75, the enthalpy change is 1487.7/0.75 and the
TI = 4501373.2 = 1.21, enthalpy balance is rearranged to
P,l = 15/88.2 = 0.17,
Pa = 66t88.2 = 0.75,
:. AS; = 0.15,
AH; = 0.2(373.2) = 75.0, Trial T, AH;
66 T2 rhs
7
- 1.9871n-+ 0.15 -AS; = 0, (1)
15 680 1.82 109 +91.7
1.80
112
-0.021
670.79
L 670.80 1.80 +0.075
rT2
Cp dT + 75.0 - AH;.
AH, = (2)
:. = 670.79 K.
1. Assume a value of T2.
2. Evaluate r2 and AS;. For ideal gas
3. Integrate Eq. (1) numerically and note the righthand side.
4. Continue with trial values of T, until AS = 0.
5. Find AH; and finally evaluate AH,.
Two trials are shown. By trial:
T2 Tr2 AS; AS AH; A% T, = 670.49 K
600 1.61 0.2 -0.047
626.6 1.68 0.2 +0.00009 187 1487.7 Nonideality is slight in this example.