Page 253 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 253
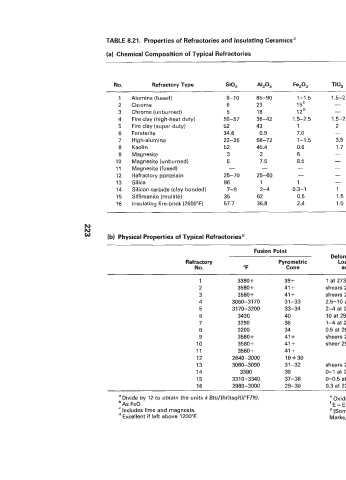
TABLE 8.21. Properties of Refractories and Insulating Ceramics"
(a) Chemical Composition of Typical Refractories
Resistance to
! Alumina (fused) 8-10 85-90 1-1.5 1.5-2.2 - 0.8-1.3=
2 Chrome 6 23 15b _I 17 38 -
3 Chrome (unburned) 5 18 12b - 32 30 -
4 Fire clay (high-heat duty) 50-57 36-42 1.5-2.5 1.5-2.5 - - 1-3.5'
5 Fire clay (super-duty) 52 43 1 2 - - 2'
6 Forsterite 34.6 0.9 7.0 - 1.3 55.4
7 High-alumina 22-26 68-72 1-1.5 3.5 - - 1-1.5c G F F F
8 Kaolin 52 45.4 0.6 1.7 0.1 0.2 - F P Gd F
S Mag iiesite 3 2 6 3 86 P E E E
10 Magnesite (unburned) 5 7.5 8.5 2 64 P E E E
11 Magnesite (fused) - - - - - F E E E
12 Refractory porcelain 25-70 25-60 - - G F F F
13 Silica 96 1 1 - 2 - E P F P
14 Silicon carbide (clay bonded) 7-9 2-4 0.3-1 1 - 85-90 E G F E
15 Sillimanite (mullite) 35 62 0.5 1.5 - - - G F F F
16 Insulating fire-brick (2600°F) 57.7 36.8 2.4 1.5 0.6 0.5 P P G" P
Fusion Point wt. of
Deformation under Repeat Shrinkage Straight
Refractory Pyrometric Load (% at "F Spalling after 5 hr 9 in.
No. "F Cone and Ib/in.) Resistancef (% "F) Brick (Ib)
1 3390+ 39 + 1 at 2730 and 50 G +0.5 (2910) 9-10.6
2 3580+ 41 + shears 2740 and 28 P -0.5-1 .O (3000) 11.0
3 3580+ 41 + shears 2955 and 28 F -0.5-1 .O (3000) 11.3
4 3060-3170 31-33 2.5-10 at 2460 and 25 G f0-1.5 (2550) 7.5
5 31 70-3200 33-34 2-4 at 2640 and 25 E f0-1.5 (2910) 8.5
6 3430 40 10 at 2950 F - 9.0
7 3290 36 1-4 at 2640 and 25 E -2-4 (2910) 7.5
8 3200 34 0.5 at 2640 and 25 E -0.7-1.0 (2910) 7.7
9 3580+ 41 + shears 2765 and 28 P -1-2 (3000) 10.0
10 3580 + 41 + shear 2940 and 28 F -0.5-1.5 (3000) 10.7
11 3580+ 41 + F - 10.5
12 2640-3000 16+30 G
13 3060-3090 31-32 shears 2900 and 25 P +0.5-0.8 (2640) 6.5
14 3390 39 0-1 at 2730 and 50 E +2 (2910) 8-9.3
15 331 0-3340 37-38 0-0.5 at 2640 and 25 E -0-0.8 (2910) 8.5
16 2 9 8 0 - 3 0 0 0 29-30 0.3 at 2200 and 10 G -0.2 (2600) 2.25
"Divide by 12 to obtain the units k Btu/(hr)(sqft)("F/ft). e Oxidizing atmosphere.
bAs FeO. E = Excellent. G = Good. F = Fair. P = Poor.
Includes lime and magnesia. '[Some data from Trostel, Chem. Met. Eng. (Nov. 1938)l.
Excellent if left above 1200°F. Marks, Mechanical Engineers Handbook, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978, pp. 6.172-6.173.