Page 398 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 398
12.5. PARTICLE SIZE ENLARGEMENT 361
I
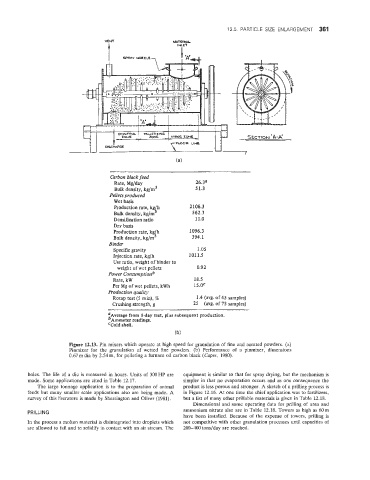
Carbon black feed
Rate, Mg/day 26.3a
Bulk density, kg/m3 5 1.3
Pellets produced
Wet basis
4
Production rate, kg h 2108.3
Bulk density, kg/m 562.3
Densification ratio 11.0
Dry basis
!!
Production rate, kg h 1096.3
Bulk density, kg/m 394.1
Binder
Specific gravity 1.05
Injection rate, kg/h 1011.5
Use ratio, weight of binder to
weight of wet pellets 0.92
power Consurnptionb
Rate, kW 18.5
Per Mg of wet pellets, kWh 15.OC
Production quolity
Rotap test (5 min), % 1.4 (avg. of45 samples)
Crushing strength, g 25 (avg. of 73 samples)
:Average from 5-day test, plus subsequent production.
Ammeter readings.
'Cold shell.
b)
Figure 12.W. Pin mixers which operate at high speed for granulation of fine and aerated powders. (a)
Pinmixer for the granulation of wetted fine powders. (b) Performance of a pinmixer, dimensions
0.67 rn dia by 2.54 m, for pelleting a furnace oil carbon black (Capes, 1980).
holes. The life of a die is measured in hours. Units of 300HP are equipment is similar to that for spray drying, but the mechanism is
made. Some aplplicaticlns are cited in Table 12.17. simpler in that no evaporation occurs and as one consequence the
The large tonnage application is to the preparation of animal product is less porous and stronger. A sketch of a prilling process is
feeds but many smaller scale applications also are being made. A in Figure 12.16. At one time the chief application was to fertilizers,
survey of this literature is made by Sherrington and Oliver (1981). but a list of many other prillable materials is given in Table 12.18.
Dimensional and some operating data for prilling of urea and
ammonium nitrate also are in Table 12.18. Towers as high as 60 m
PRILLING
have been installed. Because of the expense of towers, prilling is
In the process a molten material is disintegrated into droplets which not competitive with other granulation processes until capacities of
are allowed to fall and to solidify in contact with an air stream. The 200-400 tonslday are reached.