Page 89 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 89
4
RIVERS FOR MOVING EQUIPMENT
owered chemical processing equipment includes internal combustion engines, and direct current motors are
pumps, compressors, agitators and mixers, crushers capable of continuous speed adjustment over a wide range.
and grinders, and conveyors Drivers are electric Energy efficiencies vary widely with the size and type of
motors, steam or gas turbines, and internal driver as shown in this table.
combustion engines For loads under 150 HP or so electric
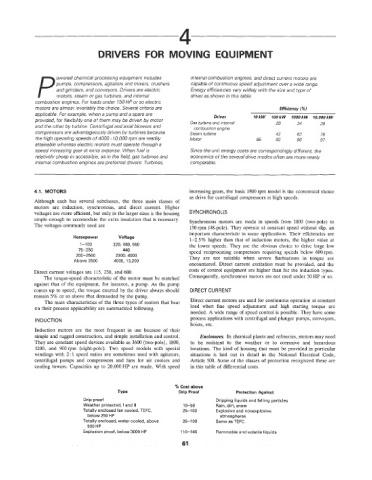
motors are almost invariably the choice Several criteria are Efficiency (%)
appkable For example, when a pump and a spare are Driver lOkW 100kW lOOOkW 10,000kW
provided, for Ilexibility one of them may be driven by motor Gas turbine and internal 28 34 38
and the other by turbine Centrifugal and axial blowers and cornbustion engine
compressors are advantageously driven by turbines because Steam turbine 42 63 78
the high operatmg speeds of 4000-10.000 rpm are readily Motor 85 92 96 97
attainable whereas electnc motors must operate through a
speed increasing gear at gxtra expense When fuel is Since the unit energy costs are correspondingly different, the
relatively cheap or accessible, as in the field, gas turbines and economics of the several drive modes often are more nearly
internal combustion engines are preferred drivers Turbines, comparable.
4.1. MOTORS increasing gears, the basic 1800 rpm model is the economical choice
as drive for centrifugal compressors at high speeds.
Although each has several subclasses, the three main classes of
motors are induction, synchronous, and direct current. Higher
voltages are more efficient, but only in the larger sizes is the housing SYNCHRONOUS
ample enough to accomodate the extra insulation that is necessary. Synchronous motors are made in speeds from I800 (two-pole) to
The voltages commonly used are 150 rpm (48-pole). They operate at constant speed without slip, an
important characteristic in some applications. Their efficiencies are
Horsepower Voltage 1-2.5% higher than that of induction motors, the higher value at
'i--?oa 220,440,550 the lower speeds. They are the obvious choice to drive large low
75-250 440 speed reciprocating compressors requiring speeds below 600 rpm.
200-2500 2300, 4000 They are not suitable when severe fluctuations in torque are
Above 2500 4000, 13,200
encountered. Direct current excitation must be provided, and the
Direct current voltages are 115, 230, and 600. costs of control equipment are higher than for the induction types.
The torque-speed characteristic of the motor must be matched Consequently, synchronous motors are not used under 50 HP or so.
against that of the equipment, for instance, a pump. As the pump
comes up to speed, the torque exerted by the driver always should DIRECT CURRENT
remain 5% or so above that demanded by the pump.
The main characteristics of the three types of motors that bear Direct current motors are used for continuous operation at constant
on their process applicability are summarized following. load when fine speed adjustment and high starting torque are
needed. A wide range of speed control is possible. They have some
IN DU CTl ON process applications with centrifugal and plunger pumps, conveyors,
hoists, etc.
Induction motors are the most frequent in use because of their
simple and rugged construction, and simple installation and control. Enclosures. In chemical plants and refineries, motors may need
They are constant speed devices available as 3600 (two-pole), 1800, to be resistant to the weather or to corrosive and hazardous
1200, and 900rpm (eight-pole). Two speed models with special locations. The kind of housing that must be provided in particular
windings with 2: 1 speed ratios are sometimes used with agitators, situations is laid out in detail in the National Electrical Code,
centrifugal pumps and compressors and fans for air coolers and Article 500. Some of the classes of protection recognized there are
cooling towers. Capacities up to 20,000HP are made. With speed in this table of differential costs.
% Cost above
Type Drip Proof Protection Against
Drip proof Dripping liquids and falling particles
Weather protected, I and II 10-50 Rain, dirt, snow
Totally enclosed fan cooled, TEFC, 25-100 Explosive and nonexplosive
below 250 HP atmospheres
Totally enclosed, water cooled, above 25-1 00 Same as TEFC
500 HP
Explosion proof, below 3000 HP 110-140 Flammable and volatile liquids
61