Page 84 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 84
56 PROCESS CONTROL
Feed
A I I
HTM
-
iTM
Product
la) Product
r
(C) + Product
I
$)+&-(&
Reset
HTM
HTM
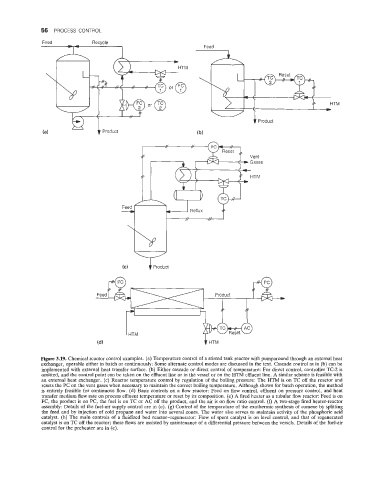
Figure 3.19. Chemical reactor control examples. (a) Temperature control of a stirred tank reactor with pumparound through an external heat
exchanger, operable either in batch or continuously: Some alternate control modes are discussed in the text. Cascade control as in (b) can be
implemented with external heat transfer surface. (b) Either cascade or- direct control of temperature: For direct control, controller TC-2 is
omitted, and the control point can be taken on the effluent line or in the vessel or on the HTM effluent line. A similar scheme is feasible with
an external heat exchanger. (c) Reactor temperature control by regulation of the boiling pressure: The HTM is on TC off the reactor and
resets the PC on the vent gases when necessary to maintain the correct boiling temperature. Although shown for batch operation, the method
is entirely feasible for continuous flow. (d) Basic controls on a flow reactor: Feed on flow control, effluent on pressure control, and heat
transfer medium flow rate on process effluent temperature or reset by its composition. (e) A fired heater as a tubular flow reactor: Feed is on
FC, the product is on PC, the fuel is on TC or AC off the product, and the air is on flow ratio control. (f) A two-stage fired heater-reactor
assembly: Details of the fuel-air supply control are in (e). (g) Control of the temperature of the exothermic synthesis of cumene by splitting
the feed and by injection of cold propane and water into several zones. The water also serves to maintain activity of the phosphoric acid
catalyst. (h) The main controls of a fluidized bed reactor-regenerator: Flow of spent catalyst is on level control, and that of regenerated
catalyst is on TC off the reactor; these flows are assisted by maintenance of a differential pressure between the vessels. Details of the fuel-air
control for the preheater are in (e).