Page 331 - Classification Parameter Estimation & State Estimation An Engg Approach Using MATLAB
P. 331
320 WORKED OUT EXAMPLES
observed waveform w(t)
↑
ToF
0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02
t(s)
zoomed
waveform τ = ToF
generator w(t)
↑
vτ ToF
8.5 9 9.5 10
t(ms)
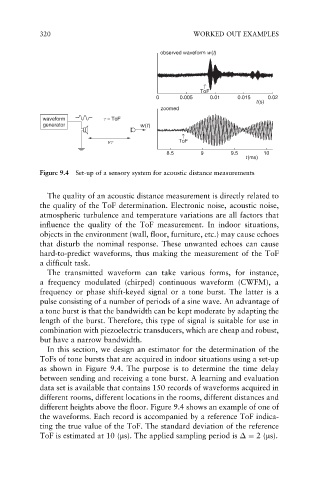
Figure 9.4 Set-up of a sensory system for acoustic distance measurements
The quality of an acoustic distance measurement is directly related to
the quality of the ToF determination. Electronic noise, acoustic noise,
atmospheric turbulence and temperature variations are all factors that
influence the quality of the ToF measurement. In indoor situations,
objects in the environment (wall, floor, furniture, etc.) may cause echoes
that disturb the nominal response. These unwanted echoes can cause
hard-to-predict waveforms, thus making the measurement of the ToF
a difficult task.
The transmitted waveform can take various forms, for instance,
a frequency modulated (chirped) continuous waveform (CWFM), a
frequency or phase shift-keyed signal or a tone burst. The latter is a
pulse consisting of a number of periods of a sine wave. An advantage of
a tone burst is that the bandwidth can be kept moderate by adapting the
length of the burst. Therefore, this type of signal is suitable for use in
combination with piezoelectric transducers, which are cheap and robust,
but have a narrow bandwidth.
In this section, we design an estimator for the determination of the
ToFs of tone bursts that are acquired in indoor situations using a set-up
as shown in Figure 9.4. The purpose is to determine the time delay
between sending and receiving a tone burst. A learning and evaluation
data set is available that contains 150 records of waveforms acquired in
different rooms, different locations in the rooms, different distances and
different heights above the floor. Figure 9.4 shows an example of one of
the waveforms. Each record is accompanied by a reference ToF indica-
ting the true value of the ToF. The standard deviation of the reference
ToF is estimated at 10 (ms). The applied sampling period is ¼ 2(ms).