Page 232 - Communication and the Evolution of Society
P. 232
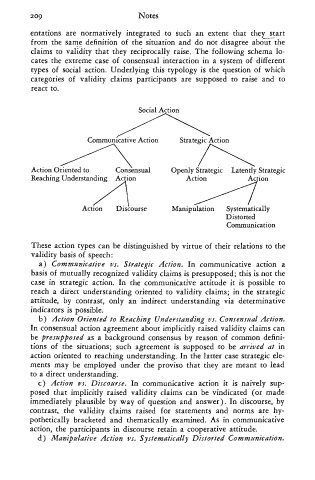
209 Notes
from the same definition of the situation and do not disagree about the
claims to validity that they reciprocally raise. The following schema lo-
cates the extreme case of consensual interaction in a system of different
types of social action. Underlying this typology is the question of which
categories of validity claims participants are supposed to raise and to
react to.
Social Action
oN Action ae
Action Oriented to Consensual Openly Strategic Latently Strategic
Reaching OS eT
Action — Discourse Manipulation Systematically
Distorted
Communication
These action types can be distinguished by virtue of their relations to the
validity basis of speech:
a) Communicative vs. Strategic Action. In communicative action a
basis of mutually recognized validity claims is presupposed; this is not the
case in strategic action. In the communicative attitude it is possible to
reach a direct understanding oriented to validity claims; in the strategic
attitude, by contrast, only an indirect understanding via determinative
indicators is possible.
b) Action Oriented to Reaching Understanding vs. Consensual Action.
In consensual action agreement about implicitly raised validity claims can
be presupposed as a background consensus by reason of common defini-
tions of the situations; such agreement is supposed to be arrived at in
action oriented to reaching understanding. In the latter case strategic ele-
ments may be employed under the proviso that they are meant to lead
to a direct understanding.
c) Action vs. Discourse. In communicative action it is naively sup-
posed that implicitly raised validity claims can be vindicated (or made
immediately plausible by way of question and answer). In discourse, by
contrast, the validity claims raised for statements and norms are hy-
pothetically bracketed and thematically examined. As in communicative
action, the participants in discourse retain a cooperative attitude.
d) Manipulative Action vs. Systematically Distorted Communication.