Page 228 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 228
3 Type of lesions/clinical features 225
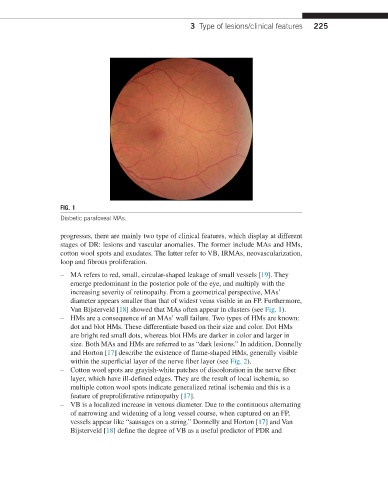
FIG. 1
Diabetic parafoveal MAs.
progresses, there are mainly two type of clinical features, which display at different
stages of DR: lesions and vascular anomalies. The former include MAs and HMs,
cotton wool spots and exudates. The latter refer to VB, IRMAs, neovascularization,
loop and fibrous proliferation.
– MA refers to red, small, circular-shaped leakage of small vessels [19]. They
emerge predominant in the posterior pole of the eye, and multiply with the
increasing severity of retinopathy. From a geometrical perspective, MAs’
diameter appears smaller than that of widest veins visible in an FP. Furthermore,
Van Bijsterveld [18] showed that MAs often appear in clusters (see Fig. 1).
– HMs are a consequence of an MAs’ wall failure. Two types of HMs are known:
dot and blot HMs. These differentiate based on their size and color. Dot HMs
are bright red small dots, whereas blot HMs are darker in color and larger in
size. Both MAs and HMs are referred to as “dark lesions.” In addition, Donnelly
and Horton [17] describe the existence of flame-shaped HMs, generally visible
within the superficial layer of the nerve fiber layer (see Fig. 2).
– Cotton wool spots are grayish-white patches of discoloration in the nerve fiber
layer, which have ill-defined edges. They are the result of local ischemia, so
multiple cotton wool spots indicate generalized retinal ischemia and this is a
feature of preproliferative retinopathy [17].
– VB is a localized increase in venous diameter. Due to the continuous alternating
of narrowing and widening of a long vessel course, when captured on an FP,
vessels appear like “sausages on a string.” Donnelly and Horton [17] and Van
Bijsterveld [18] define the degree of VB as a useful predictor of PDR and