Page 178 -
P. 178
148 CHAPTER 4 / CACHE MEMORY
All four lines in No Replace
the set valid? nonvalid line
Yes
B0 0?
Yes, L0 or L1 No, L2 or L3
least recently used least recently used
B1 0? B2 0?
Yes No Yes No
Replace Replace Replace Replace
L0 L1 L2 L3
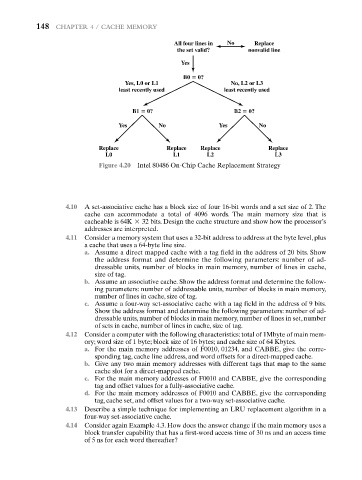
Figure 4.20 Intel 80486 On-Chip Cache Replacement Strategy
4.10 A set-associative cache has a block size of four 16-bit words and a set size of 2. The
cache can accommodate a total of 4096 words. The main memory size that is
cacheable is 64K * 32 bits. Design the cache structure and show how the processor’s
addresses are interpreted.
4.11 Consider a memory system that uses a 32-bit address to address at the byte level, plus
a cache that uses a 64-byte line size.
a. Assume a direct mapped cache with a tag field in the address of 20 bits. Show
the address format and determine the following parameters: number of ad-
dressable units, number of blocks in main memory, number of lines in cache,
size of tag.
b. Assume an associative cache. Show the address format and determine the follow-
ing parameters: number of addressable units, number of blocks in main memory,
number of lines in cache, size of tag.
c. Assume a four-way set-associative cache with a tag field in the address of 9 bits.
Show the address format and determine the following parameters: number of ad-
dressable units, number of blocks in main memory, number of lines in set, number
of sets in cache, number of lines in cache, size of tag.
4.12 Consider a computer with the following characteristics: total of 1Mbyte of main mem-
ory; word size of 1 byte; block size of 16 bytes; and cache size of 64 Kbytes.
a. For the main memory addresses of F0010, 01234, and CABBE, give the corre-
sponding tag, cache line address, and word offsets for a direct-mapped cache.
b. Give any two main memory addresses with different tags that map to the same
cache slot for a direct-mapped cache.
c. For the main memory addresses of F0010 and CABBE, give the corresponding
tag and offset values for a fully-associative cache.
d. For the main memory addresses of F0010 and CABBE, give the corresponding
tag, cache set, and offset values for a two-way set-associative cache.
4.13 Describe a simple technique for implementing an LRU replacement algorithm in a
four-way set-associative cache.
4.14 Consider again Example 4.3. How does the answer change if the main memory uses a
block transfer capability that has a first-word access time of 30 ns and an access time
of 5 ns for each word thereafter?