Page 237 -
P. 237
204 CHAPTER 6 / EXTERNAL MEMORY
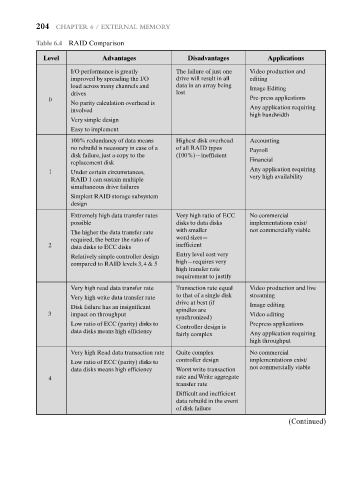
Table 6.4 RAID Comparison
Level Advantages Disadvantages Applications
I/O performance is greatly The failure of just one Video production and
improved by spreading the I/O drive will result in all editing
load across many channels and data in an array being Image Editing
drives lost
0 Pre-press applications
No parity calculation overhead is
Any application requiring
involved
high bandwidth
Very simple design
Easy to implement
100% redundancy of data means Highest disk overhead Accounting
no rebuild is necessary in case of a of all RAID types Payroll
disk failure, just a copy to the (100%)—inefficient
replacement disk Financial
1 Under certain circumstances, Any application requiring
RAID 1 can sustain multiple very high availability
simultaneous drive failures
Simplest RAID storage subsystem
design
Extremely high data transfer rates Very high ratio of ECC No commercial
possible disks to data disks implementations exist/
The higher the data transfer rate with smaller not commercially viable
required, the better the ratio of word sizes—
2 data disks to ECC disks inefficient
Relatively simple controller design Entry level cost very
compared to RAID levels 3, 4 & 5 high—requires very
high transfer rate
requirement to justify
Very high read data transfer rate Transaction rate equal Video production and live
to that of a single disk streaming
Very high write data transfer rate
drive at best (if
Disk failure has an insignificant Image editing
spindles are
3 impact on throughput Video editing
synchronized)
Low ratio of ECC (parity) disks to Prepress applications
Controller design is
data disks means high efficiency
fairly complex Any application requiring
high throughput
Very high Read data transaction rate Quite complex No commercial
Low ratio of ECC (parity) disks to controller design implementations exist/
data disks means high efficiency Worst write transaction not commercially viable
4 rate and Write aggregate
transfer rate
Difficult and inefficient
data rebuild in the event
of disk failure
(Continued)