Page 238 -
P. 238
6.3 / OPTICAL MEMORY 205
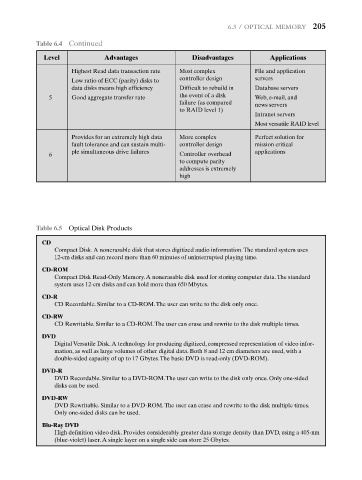
Table 6.4 Continued
Level Advantages Disadvantages Applications
Highest Read data transaction rate Most complex File and application
Low ratio of ECC (parity) disks to controller design servers
data disks means high efficiency Difficult to rebuild in Database servers
5 Good aggregate transfer rate the event of a disk Web, e-mail, and
failure (as compared news servers
to RAID level 1)
Intranet servers
Most versatile RAID level
Provides for an extremely high data More complex Perfect solution for
fault tolerance and can sustain multi- controller design mission critical
ple simultaneous drive failures applications
6 Controller overhead
to compute parity
addresses is extremely
high
Table 6.5 Optical Disk Products
CD
Compact Disk.A nonerasable disk that stores digitized audio information.The standard system uses
12-cm disks and can record more than 60 minutes of uninterrupted playing time.
CD-ROM
Compact Disk Read-Only Memory.A nonerasable disk used for storing computer data.The standard
system uses 12-cm disks and can hold more than 650 Mbytes.
CD-R
CD Recordable. Similar to a CD-ROM.The user can write to the disk only once.
CD-RW
CD Rewritable. Similar to a CD-ROM.The user can erase and rewrite to the disk multiple times.
DVD
Digital Versatile Disk.A technology for producing digitized, compressed representation of video infor-
mation, as well as large volumes of other digital data. Both 8 and 12 cm diameters are used, with a
double-sided capacity of up to 17 Gbytes.The basic DVD is read-only (DVD-ROM).
DVD-R
DVD Recordable. Similar to a DVD-ROM.The user can write to the disk only once. Only one-sided
disks can be used.
DVD-RW
DVD Rewritable. Similar to a DVD-ROM.The user can erase and rewrite to the disk multiple times.
Only one-sided disks can be used.
Blu-Ray DVD
High definition video disk. Provides considerably greater data storage density than DVD, using a 405-nm
(blue-violet) laser.A single layer on a single side can store 25 Gbytes.