Page 722 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 722
674 C h a p t e r 1 5 H i g h - Te m p e r a t u r e C o r r o s i o n 675
0 Cr S
2 3
Cr (SO )
4 3
2
CrS
–10
Log pS 2 (g) –20 Cr O 3
2
Cr
–30
CrO 2
–40
–50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0 10
Log pO 2
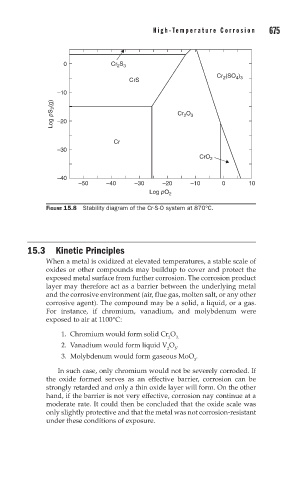
FIGURE 15.8 Stability diagram of the Cr-S-O system at 870°C.
15.3 Kinetic Principles
When a metal is oxidized at elevated temperatures, a stable scale of
oxides or other compounds may buildup to cover and protect the
exposed metal surface from further corrosion. The corrosion product
layer may therefore act as a barrier between the underlying metal
and the corrosive environment (air, flue gas, molten salt, or any other
corrosive agent). The compound may be a solid, a liquid, or a gas.
For instance, if chromium, vanadium, and molybdenum were
exposed to air at 1100°C:
1. Chromium would form solid Cr O
2 3.
2. Vanadium would form liquid V O .
2 5
3. Molybdenum would form gaseous MoO .
3
In such case, only chromium would not be severely corroded. If
the oxide formed serves as an effective barrier, corrosion can be
strongly retarded and only a thin oxide layer will form. On the other
hand, if the barrier is not very effective, corrosion nay continue at a
moderate rate. It could then be concluded that the oxide scale was
only slightly protective and that the metal was not corrosion-resistant
under these conditions of exposure.