Page 88 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 88
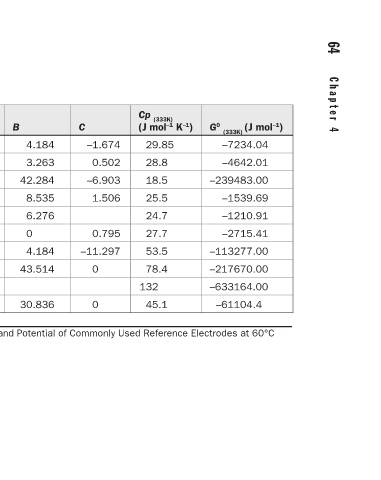
64 C h a p t e r 4 C o r r o s i o n T h e r m o d y n a m i c s 65
G 0 (333K) (J mol –1 ) –7234.04 –4642.01 –239483.00 –1539.69 –1210.91 –2715.41 –113277.00 –217670.00 –633164.00 –61104.4
Cp (333K) (J mol –1 K –1 ) 29.85 28.8 18.5 25.5 24.7 27.7 53.5 78.4 132 45.1
–1.674 0.502 –6.903 1.506 0.795 –11.297 0 0
C
4.184 3.263 42.284 8.535 6.276 0 4.184 43.514 30.836
B Thermodynamic Data for Pure Species, the Free Energy, and Potential of Commonly Used Reference Electrodes at 60°C
29.96 27.28 10.669 21.297 22.635 26.94 62.258 63.932 131.96 34.853
A
S 0 (298 K) (J mol –1 ) 205 131 69.9 42.55 33.2 76.02 96.2 192.5 200.66 70.29
G 0 (298 K) (J mol –1 ) 0 0 −237000 0 0 0 –109805 –210778 –625880 –58555
Species O 2 H 2 H 2 O Ag Cu Hg AgCl Hg 2 Cl 2 Hg 2 SO 4 HgO TABLE 4.8