Page 308 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 308
7.5 Scheduling Formulations 293
A schedule is processor optimal if it uses as minimum number of PEs of each
type. The minimum number of PEs of type i, called the processor bound, is
where D op j is the total execution time for all operations of type i and T mi n is the
minimal sample period.
7.5 SCHEDULING FORMULATIONS
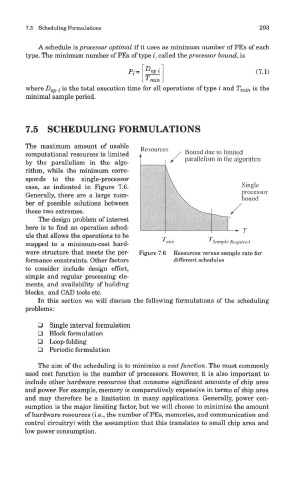
The maximum amount of usable
computational resources is limited
by the parallelism in the algo-
rithm, while the minimum corre-
sponds to the single-processor
case, as indicated in Figure 7.6.
Generally, there are a large num-
ber of possible solutions between
these two extremes.
The design problem of interest
here is to find an operation sched-
ule that allows the operations to be
mapped to a minimum-cost hard-
ware structure that meets the per- Figure 7.6 Resources versus sample rate for
formance constraints. Other factors different schedules
to consider include design effort,
simple and regular processing ele-
ments, and availability of building
blocks, and CAD tools etc.
in this section we will discuss tne following formulations or tne scheduling
problems:
Q Single interval formulation
Q Block formulation
Q Loop-folding
Q Periodic formulation
The aim of the scheduling is to minimize a cost function. The most commonly
used cost function is the number of processors. However, it is also important to
include other hardware resources that consume significant amounts of chip area
and power. For example, memory is comparatively expensive in terms of chip area
and may therefore be a limitation in many applications. Generally, power con-
sumption is the major limiting factor, but we will choose to minimize the amount
of hardware resources (i.e., the number of PEs, memories, and communication and
control circuitry) with the assumption that this translates to small chip area and
low power consumption.