Page 97 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 97
82 Chapter 3 Digital Signal Processing
direction of all branches in a signal-flow graph and changing inputs to outputs and
vice versa. This new filter structure has the same transfer function as the original
filter, but the numerical properties are generally different.
Theorem 3.2—Transposition
The transfer function of a signal-flow graph is invariant if the direction of
all branches is reversed and the inputs and outputs are interchanged.
A dual network performs the complementary function of the original network
[15]. For example, demodulators and modulators are dual operations. Given a net-
work, its dual is found by transposing the network. Any linear time-invariant net-
work has a dual. Interpolators and decimators, which will be further discussed in
Chapter 4, perform dual operations.
Two operations are said to be commutating if the result is independent of the
order in which the operations are performed. We will later show that, in some
cases, changing the order of two operations can provide significant computational
savings [15].
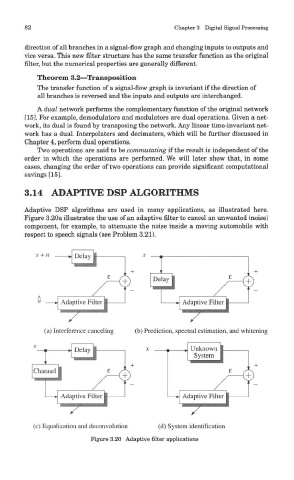
3.14 ADAPTIVE DSP ALGORITHMS
Adaptive DSP algorithms are used in many applications, as illustrated here.
Figure 3.20a illustrates the use of an adaptive filter to cancel an unwanted (noise)
component, for example, to attenuate the noise inside a moving automobile with
respect to speech signals (see Problem 3.21).
Figure 3.20 Adaptive filter applications