Page 296 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 296
256 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
Identification of critical
PQ buses with aid TV
Generators closest to each
Generator identification
critical bus are selected
Calculation of TV mod for
each candidate generator
The most influential
generators for each bus
Initial particle swarm
Calculation of active
power losses No
Determine y and obtain Stop criterion
i
reached?
Actualize the velocity of
each particle Yes
Minimized active power
Actualize the position of
losses PSO
each particle
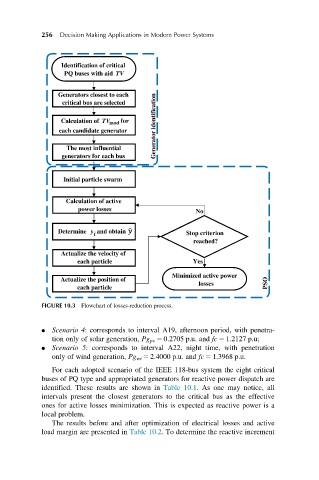
FIGURE 10.3 Flowchart of losses-reduction process.
Scenario 4: corresponds to interval A19, afternoon period, with penetra-
tion only of solar generation, Pg pv 5 0.2705 p.u. and fc 5 1.2127 p.u;
Scenario 5: corresponds to interval A22, night time, with penetration
only of wind generation, Pg wt 5 2.4000 p.u. and fc 5 1.3968 p.u.
For each adopted scenario of the IEEE 118-bus system the eight critical
buses of PQ type and appropriated generators for reactive power dispatch are
identified. These results are shown in Table 10.1. As one may notice, all
intervals present the closest generators to the critical bus as the effective
ones for active losses minimization. This is expected as reactive power is a
local problem.
The results before and after optimization of electrical losses and active
load margin are presented in Table 10.2. To determine the reactive increment