Page 409 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 409
6.60 CHAPTER SIX
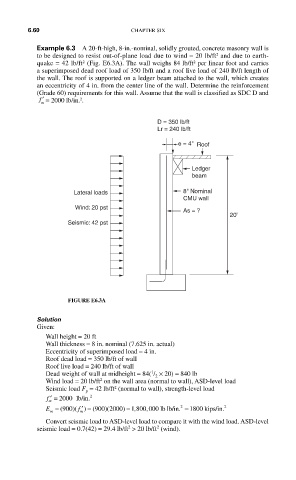
Example 6.3 A 20-ft-high, 8-in.-nominal, solidly grouted, concrete masonry wall is
2
to be designed to resist out-of-plane load due to wind = 20 lb/ft and due to earth-
2
2
quake = 42 lb/ft (Fig. E6.3A). The wall weighs 84 lb/ft per linear foot and carries
a superimposed dead roof load of 350 lb/ft and a roof live load of 240 lb/ft length of
the wall. The roof is supported on a ledger beam attached to the wall, which creates
an eccentricity of 4 in. from the center line of the wall. Determine the reinforcement
(Grade 60) requirements for this wall. Assume that the wall is classified as SDC D and
2
′ f = 2000 lb/in. .
m
D = 350 lb/ft
Lr = 240 lb/ft
e = 4" Roof
Ledger
beam
Lateral loads 8" Nominal
CMU wall
Wind: 20 pst
As = ?
20'
Seismic: 42 pst
FIGURE E6.3A
Solution
Given:
Wall height = 20 ft
Wall thickness = 8 in. nominal (7.625 in. actual)
Eccentricity of superimposed load = 4 in.
Roof dead load = 350 lb/ft of wall
Roof live load = 240 lb/ft of wall
1
Dead weight of wall at midheight = 84( / × 20) = 840 lb
2
2
Wind load = 20 lb/ft on the wall area (normal to wall), ASD-level load
Seismic load F = 42 lb/ft (normal to wall), strength-level load
2
p
f m ′ = 2000 lb/in. 2
2 2
)
E = (900 )( f ′ = (900 )(2000 ) = ,800 000 lb lb/in. = 1800 kips/in. 2
1
,
m m
Convert seismic load to ASD-level load to compare it with the wind load. ASD-level
2
2
seismic load = 0.7(42) = 29.4 lb/ft > 20 lb/ft (wind).