Page 101 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 101
72 Cha pte r T w o
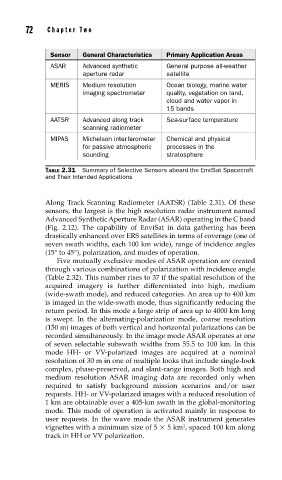
Sensor General Characteristics Primary Application Areas
ASAR Advanced synthetic General purpose all-weather
aperture radar satellite
MERIS Medium resolution Ocean biology, marine water
imaging spectrometer quality, vegetation on land,
cloud and water vapor in
15 bands
AATSR Advanced along track Sea-surface temperature
scanning radiometer
MIPAS Michelson interferometer Chemical and physical
for passive atmospheric processes in the
sounding stratosphere
TABLE 2.31 Summary of Selective Sensors aboard the EnviSat Spacecraft
and Their Intended Applications
Along Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) (Table 2.31). Of these
sensors, the largest is the high resolution radar instrument named
Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) operating in the C band
(Fig. 2.12). The capability of EnviSat in data gathering has been
drastically enhanced over ERS satellites in terms of coverage (one of
seven swath widths, each 100 km wide), range of incidence angles
(15° to 45°), polarization, and modes of operation.
Five mutually exclusive modes of ASAR operation are created
through various combinations of polarization with incidence angle
(Table 2.32). This number rises to 37 if the spatial resolution of the
acquired imagery is further differentiated into high, medium
(wide-swath mode), and reduced categories. An area up to 400 km
is imaged in the wide-swath mode, thus significantly reducing the
return period. In this mode a large strip of area up to 4000 km long
is swept. In the alternating-polarization mode, coarse resolution
(150 m) images of both vertical and horizontal polarizations can be
recorded simultaneously. In the image mode ASAR operates at one
of seven selectable subswath widths from 55.5 to 100 km. In this
mode HH- or VV-polarized images are acquired at a nominal
resolution of 30 m in one of multiple looks that include single-look
complex, phase-preserved, and slant-range images. Both high and
medium resolution ASAR imaging data are recorded only when
required to satisfy background mission scenarios and/or user
requests. HH- or VV-polarized images with a reduced resolution of
1 km are obtainable over a 405-km swath in the global-monitoring
mode. This mode of operation is activated mainly in response to
user requests. In the wave mode the ASAR instrument generates
2
vignettes with a minimum size of 5 5 km , spaced 100 km along
track in HH or VV polarization.