Page 97 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 97
68 Cha pte r T w o
have to change, as well. It takes up to 2 weeks for the newly configured
orbital parameters to stabilize to within 1 km of the nominal ground
track. The stabilization pace of the orbital cycle is as fast as within
5 km after 24 hours.
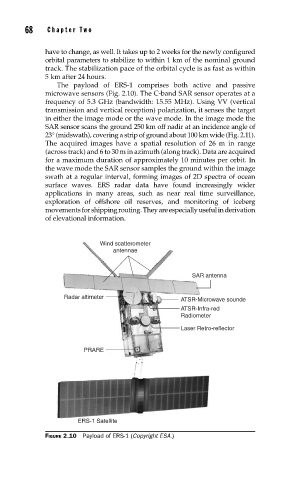
The payload of ERS-1 comprises both active and passive
microwave sensors (Fig. 2.10). The C-band SAR sensor operates at a
frequency of 5.3 GHz (bandwidth: 15.55 MHz). Using VV (vertical
transmission and vertical reception) polarization, it senses the target
in either the image mode or the wave mode. In the image mode the
SAR sensor scans the ground 250 km off nadir at an incidence angle of
23° (midswath), covering a strip of ground about 100 km wide (Fig. 2.11).
The acquired images have a spatial resolution of 26 m in range
(across track) and 6 to 30 m in azimuth (along track). Data are acquired
for a maximum duration of approximately 10 minutes per orbit. In
the wave mode the SAR sensor samples the ground within the image
swath at a regular interval, forming images of 2D spectra of ocean
surface waves. ERS radar data have found increasingly wider
applications in many areas, such as near real time surveillance,
exploration of offshore oil reserves, and monitoring of iceberg
movementsfor shipping routing. They are especially useful in derivation
of elevational information.
Wind scatterometer
antennae
SAR antenna
Radar altimeter
ATSR-Microwave sounde
ATSR-Infra-red
Radiometer
Laser Retro-reflector
PRARE
ERS-1 Satellite
FIGURE 2.10 Payload of ERS-1 (Copyright ESA.)