Page 92 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 92
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 63
hyperspectral band is much narrower in its bandwidth. In contrast to
all the satellite programs covered in this chapter so far, the hyperspectral
sensor is either spaceborne or airborne. In this section, a spaceborne
example, Hyperion, is introduced first, followed by two airborne
examples, Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS)
and Compact Airborne Spectrographic Imager (CASI).
2.5.1 Hyperion Satellite Data
Hyperion is one of the three primary instruments aboard the Earth
Observing-1(EO-1) spacecraft that was launched on November 21,
2000. EO-1 revolves around the Earth in a circular, sun-synchronous
orbit. Inclined at 98.7°, this orbit has an altitude of 705 km. Such an
orbital setting of EO-1 matches the Landsat 7 orbit within 1 minute.
Hyperion images cover a ground area nearly identical to TM’s for the
purpose of comparison. The Hyperion telescope can be rolled by up
to 22° to view a Landsat swath next to the ground track swath. This
side-looking capability enables a given ground target to be imaged
up to 5 times during the 16-day revisit period.
As a high spatial resolution hyperspectral sensor, the Hyperion
payload consists of a single telescope, one VNIR spectrometer, and
one SWIR spectrometer. The VNIR spectrometer captures radiation
over the 0.4 to 1 μm range (Pearlman et al., 2000). The SWIR
spectrometer has an array of 160 (spectral) by 250 (spatial) channels.
Jointly, the spectral range of the instrument extends from 0.4 to 2.5 μm
with a spectral resolution of 10 nm (Table 2.25). The sensor is capable
of recording 220 contiguous spectral bands at a spatial resolution of
2
30 m on the ground, covering a ground area of 7.5 100 km at high
radiometric accuracy. All data are quantized to 12 bits.
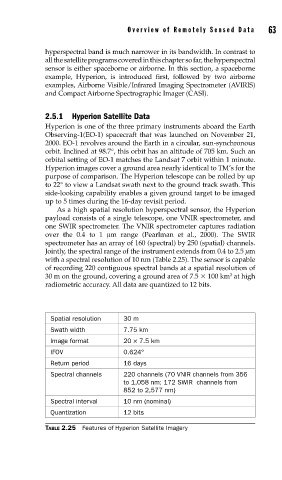
Spatial resolution 30 m
Swath width 7.75 km
Image format 20 × 7.5 km
IFOV 0.624°
Return period 16 days
Spectral channels 220 channels (70 VNIR channels from 356
to 1,058 nm; 172 SWIR channels from
852 to 2,577 nm)
Spectral interval 10 nm (nominal)
Quantization 12 bits
TABLE 2.25 Features of Hyperion Satellite Imagery