Page 216 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 216
180 Cha pte r F i v e
unuseable. More GCPs are useable with the SPOT XL image owing to
its coarse spatial resolution. If the spatial resolution degrades to 30 m
for Landsat TM imagery, a large majority of the 22 selected GCPs are
still useable.
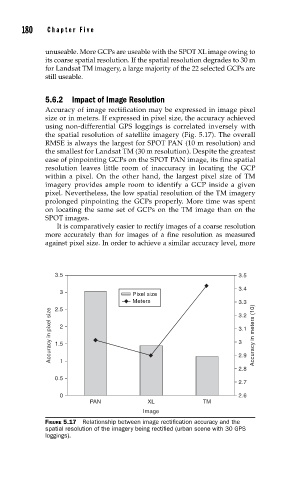
5.6.2 Impact of Image Resolution
Accuracy of image rectification may be expressed in image pixel
size or in meters. If expressed in pixel size, the accuracy achieved
using non-differential GPS loggings is correlated inversely with
the spatial resolution of satellite imagery (Fig. 5.17). The overall
RMSE is always the largest for SPOT PAN (10 m resolution) and
the smallest for Landsat TM (30 m resolution). Despite the greatest
ease of pinpointing GCPs on the SPOT PAN image, its fine spatial
resolution leaves little room of inaccuracy in locating the GCP
within a pixel. On the other hand, the largest pixel size of TM
imagery provides ample room to identify a GCP inside a given
pixel. Nevertheless, the low spatial resolution of the TM imagery
prolonged pinpointing the GCPs properly. More time was spent
on locating the same set of GCPs on the TM image than on the
SPOT images.
It is comparatively easier to rectify images of a coarse resolution
more accurately than for images of a fine resolution as measured
against pixel size. In order to achieve a similar accuracy level, more
3.5 3.5
3.4
3 Pixel size
Meters 3.3
2.5
Accuracy in pixel size 1.5 2 3.1 Accuracy in meters (10)
3.2
3
2.9
1
2.8
0.5
2.7
0 2.6
PAN XL TM
Image
FIGURE 5.17 Relationship between image rectifi cation accuracy and the
spatial resolution of the imagery being rectifi ed (urban scene with 30 GPS
loggings).