Page 220 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 220
184 Cha pte r F i v e
5.7.1 Perspective versus Orthographic Projection
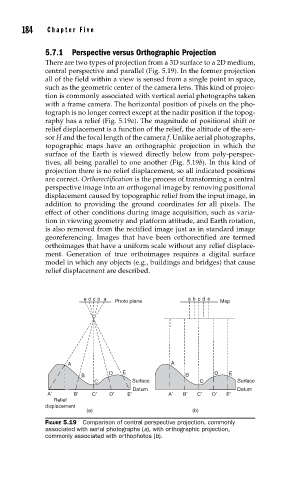
There are two types of projection from a 3D surface to a 2D medium,
central perspective and parallel (Fig. 5.19). In the former projection
all of the field within a view is sensed from a single point in space,
such as the geometric center of the camera lens. This kind of projec-
tion is commonly associated with vertical aerial photographs taken
with a frame camera. The horizontal position of pixels on the pho-
tograph is no longer correct except at the nadir position if the topog-
raphy has a relief (Fig. 5.19a). The magnitude of positional shift or
relief displacement is a function of the relief, the altitude of the sen-
sor H and the focal length of the camera f. Unlike aerial photographs,
topographic maps have an orthographic projection in which the
surface of the Earth is viewed directly below from poly-perspec-
tives, all being parallel to one another (Fig. 5.19b). In this kind of
projection there is no relief displacement, so all indicated positions
are correct. Orthorectification is the process of transforming a central
perspective image into an orthogonal image by removing positional
displacement caused by topographic relief from the input image, in
addition to providing the ground coordinates for all pixels. The
effect of other conditions during image acquisition, such as varia-
tion in viewing geometry and platform attitude, and Earth rotation,
is also removed from the rectified image just as in standard image
georeferencing. Images that have been orthorectified are termed
orthoimages that have a uniform scale without any relief displace-
ment. Generation of true orthoimages requires a digital surface
model in which any objects (e.g., buildings and bridges) that cause
relief displacement are described.
e d c b a a b c d e
Photo plane Map
A A
D E D E
B B
C Surface C Surface
Datum Datum
A′ B′ C′ D′ E′ A′ B′ C′ D′ E′
Relief
displacement
(a) (b)
FIGURE 5.19 Comparison of central perspective projection, commonly
associated with aerial photographs (a), with orthographic projection,
commonly associated with orthophotos (b).