Page 71 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 71
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 43
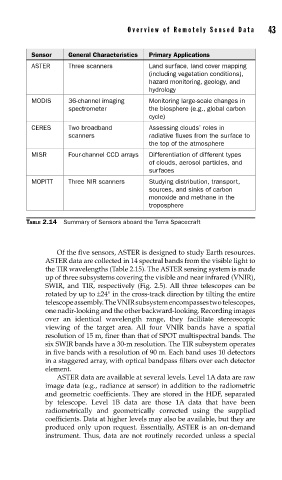
Sensor General Characteristics Primary Applications
ASTER Three scanners Land surface, land cover mapping
(including vegetation conditions),
hazard monitoring, geology, and
hydrology
MODIS 36-channel imaging Monitoring large-scale changes in
spectrometer the biosphere (e.g., global carbon
cycle)
CERES Two broadband Assessing clouds’ roles in
scanners radiative fluxes from the surface to
the top of the atmosphere
MISR Four-channel CCD arrays Differentiation of different types
of clouds, aerosol particles, and
surfaces
MOPITT Three NIR scanners Studying distribution, transport,
sources, and sinks of carbon
monoxide and methane in the
troposphere
TABLE 2.14 Summary of Sensors aboard the Terra Spacecraft
Of the five sensors, ASTER is designed to study Earth resources.
ASTER data are collected in 14 spectral bands from the visible light to
the TIR wavelengths (Table 2.15). The ASTER sensing system is made
up of three subsystems covering the visible and near infrared (VNIR),
SWIR, and TIR, respectively (Fig. 2.5). All three telescopes can be
rotated by up to ±24° in the cross-track direction by tilting the entire
telescope assembly. The VNIR subsystem encompasses two telescopes,
one nadir-looking and the other backward-looking. Recording images
over an identical wavelength range, they facilitate stereoscopic
viewing of the target area. All four VNIR bands have a spatial
resolution of 15 m, finer than that of SPOT multispectral bands. The
six SWIR bands have a 30-m resolution. The TIR subsystem operates
in five bands with a resolution of 90 m. Each band uses 10 detectors
in a staggered array, with optical bandpass filters over each detector
element.
ASTER data are available at several levels. Level 1A data are raw
image data (e.g., radiance at sensor) in addition to the radiometric
and geometric coefficients. They are stored in the HDF, separated
by telescope. Level 1B data are those 1A data that have been
radiometrically and geometrically corrected using the supplied
coefficients. Data at higher levels may also be available, but they are
produced only upon request. Essentially, ASTER is an on-demand
instrument. Thus, data are not routinely recorded unless a special