Page 66 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 66
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 39
SPOT multispectral data, with a spatial resolution slightly better
than that of Landsat TM images, have found applications in many
similar areas. They range from agriculture, forest management,
natural disaster management, to water resources management.
Thanks to the availability of finer spatial resolution panchromatic
data, they have been applied to costal studies and oceanography, as
well as urban planning, areas that are difficult to study using TM
imagery. The 3D viewing ability of SPOT data enables the production
of small-scale topographic maps in areas where useable stereoscopic
aerial photographs are difficult to obtain because of frequent cloud
blockage or areas where such photographs are nonexistent.
2.3.3 IRS Data
The third major player in remotely sensing the Earth’s surface for
resources mapping is the India National Space program. Since the
late 1980s, the IRS program has witnessed the launch of a series of
satellites with a revisit period of 22 days. The first one, IRS-1A, was
launched on March 17, 1988, followed by IRS-1B on August 29, 1991.
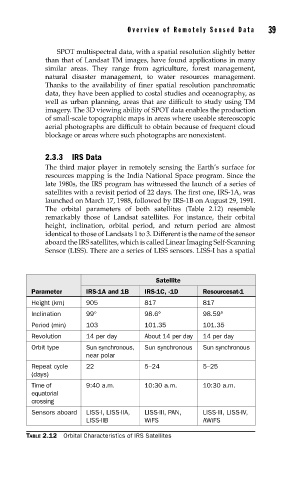
The orbital parameters of both satellites (Table 2.12) resemble
remarkably those of Landsat satellites. For instance, their orbital
height, inclination, orbital period, and return period are almost
identical to those of Landsats 1 to 3. Different is the name of the sensor
aboard the IRS satellites, which is called Linear Imaging Self-Scanning
Sensor (LISS). There are a series of LISS sensors. LISS-I has a spatial
Satellite
Parameter IRS-1A and 1B IRS-1C, -1D Resourcesat-1
Height (km) 905 817 817
Inclination 99° 98.6° 98.59°
Period (min) 103 101.35 101.35
Revolution 14 per day About 14 per day 14 per day
Orbit type Sun synchronous, Sun synchronous Sun synchronous
near polar
Repeat cycle 22 5–24 5–25
(days)
Time of 9:40 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m.
equatorial
crossing
Sensors aboard LISS-I, LISS-IIA, LISS-III, PAN, LISS-III, LISS-IV,
LISS-IIB WiFS AWiFS
TABLE 2.12 Orbital Characteristics of IRS Satellites