Page 86 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 86
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 57
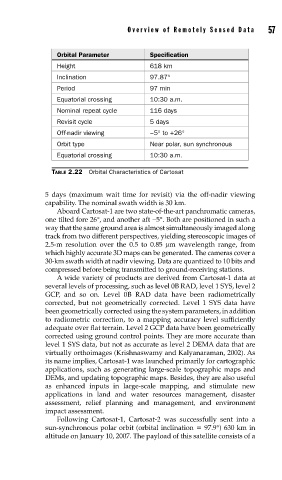
Orbital Parameter Specification
Height 618 km
Inclination 97.87°
Period 97 min
Equatorial crossing 10:30 a.m.
Nominal repeat cycle 116 days
Revisit cycle 5 days
Off-nadir viewing −5° to +26°
Orbit type Near polar, sun synchronous
Equatorial crossing 10:30 a.m.
TABLE 2.22 Orbital Characteristics of Cartosat
5 days (maximum wait time for revisit) via the off-nadir viewing
capability. The nominal swath width is 30 km.
Aboard Cartosat-1 are two state-of-the-art panchromatic cameras,
one tilted fore 26°, and another aft −5°. Both are positioned in such a
way that the same ground area is almost simultaneously imaged along
track from two different perspectives, yielding stereoscopic images of
2.5-m resolution over the 0.5 to 0.85 μm wavelength range, from
which highly accurate 3D maps can be generated. The cameras cover a
30-km swath width at nadir viewing. Data are quantized to 10 bits and
compressed before being transmitted to ground-receiving stations.
A wide variety of products are derived from Cartosat-1 data at
several levels of processing, such as level 0B RAD, level 1 SYS, level 2
GCP, and so on. Level 0B RAD data have been radiometrically
corrected, but not geometrically corrected. Level 1 SYS data have
been geometrically corrected using the system parameters, in addition
to radiometric correction, to a mapping accuracy level sufficiently
adequate over flat terrain. Level 2 GCP data have been geometrically
corrected using ground control points. They are more accurate than
level 1 SYS data, but not as accurate as level 2 DEMA data that are
virtually orthoimages (Krishnaswamy and Kalyanaraman, 2002). As
its name implies, Cartosat-1 was launched primarily for cartographic
applications, such as generating large-scale topographic maps and
DEMs, and updating topographic maps. Besides, they are also useful
as enhanced inputs in large-scale mapping, and stimulate new
applications in land and water resources management, disaster
assessment, relief planning and management, and environment
impact assessment.
Following Cartosat-1, Cartosat-2 was successfully sent into a
sun-synchronous polar orbit (orbital inclination 97.9°) 630 km in
altitude on January 10, 2007. The payload of this satellite consists of a