Page 82 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 82
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 53
its orbit when it was launched on November 20, 2000. QuickBird-2
was successfully launched into a sun-synchronous, circular orbit
450 km in altitude on October 21, 2001. It is the first commercial
satellite that is capable of gathering submeter data. Its orbit has an
inclination of 97.2° and a period of 93.45 minutes (Table 2.20). The
telescope of QuickBird-2 provides an FOV of 2.12º that can be further
extended to a pointing capability of ±30° off nadir in the along-track
and cross-track directions. At this off-nadir position, the revisit
period is reduced to 1–3.5 days, the exact period varying with latitude.
The sensor acquires high-resolution, coincident panchromatic, and
multispectral images simultaneously using pushbroom scanning.
The CCD detector comprises an array of 27,568 pixels in the cross-track
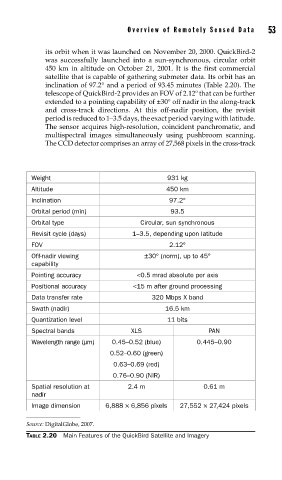
Weight 931 kg
Altitude 450 km
Inclination 97.2°
Orbital period (min) 93.5
Orbital type Circular, sun synchronous
Revisit cycle (days) 1–3.5, depending upon latitude
FOV 2.12°
Off-nadir viewing ±30° (norm), up to 45°
capability
Pointing accuracy <0.5 mrad absolute per axis
Positional accuracy <15 m after ground processing
Data transfer rate 320 Mbps X band
Swath (nadir) 16.5 km
Quantization level 11 bits
Spectral bands XLS PAN
Wavelength range (μm) 0.45–0.52 (blue) 0.445–0.90
0.52–0.60 (green)
0.63–0.69 (red)
0.76–0.90 (NIR)
Spatial resolution at 2.4 m 0.61 m
nadir
Image dimension 6,888 × 6,856 pixels 27,552 × 27,424 pixels
Source: DigitalGlobe, 2007.
TABLE 2.20 Main Features of the QuickBird Satellite and Imagery