Page 154 - Dynamic Vision for Perception and Control of Motion
P. 154
138 5 Extraction of Visual Features
If an extreme value of the magnitude of
the mask response above the threshold
level (see Figure 5.6) has been found by
stating that the new value is smaller than
the old one, the last three values are used
to find the interpolating parabola of second
order. Its extreme value yields the position
y extr of the edge to subpixel accuracy and
the corresponding magnitude C extr; this po-
sition is obtained at the location where the
derivative of the parabolic unction is zero.
Designating the largest correlation value
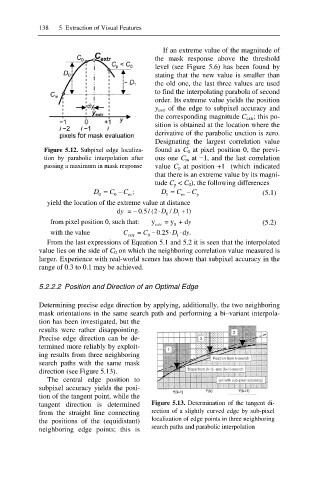
Figure 5.12. Subpixel edge localiza- found as C 0 at pixel position 0, the previ-
tion by parabolic interpolation after ous one C m at í1, and the last correlation
passing a maximum in mask response value C p at position +1 (which indicated
that there is an extreme value by its magni-
tude C p < C 0), the following differences
D = C C ; D = C C (5.1)
0 0 m 1 m p
yield the location of the extreme value at distance
d y 0.5/ (2 D / D 1)
0 1
from pixel position 0, such that: y extr = y + dy (5.2)
0
with the value C extr = C 0 0.25 D 1 d . y
From the last expressions of Equation 5.1 and 5.2 it is seen that the interpolated
value lies on the side of C 0 on which the neighboring correlation value measured is
larger. Experience with real-world scenes has shown that subpixel accuracy in the
range of 0.3 to 0.1 may be achieved.
5.2.2.2 Position and Direction of an Optimal Edge
Determining precise edge direction by applying, additionally, the two neighboring
mask orientations in the same search path and performing a bi–variant interpola-
tion has been investigated, but the
results were rather disappointing.
Precise edge direction can be de-
termined more reliably by exploit-
ing results from three neighboring
search paths with the same mask
direction (see Figure 5.13).
The central edge position to
subpixel accuracy yields the posi-
tion of the tangent point, while the
tangent direction is determined Figure 5.13. Determination of the tangent di-
from the straight line connecting rection of a slightly curved edge by sub-pixel
the positions of the (equidistant) localization of edge points in three neighboring
neighboring edge points; this is search paths and parabolic interpolation