Page 143 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 143
M03_CHAF9601_04_SE_C03.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:09 Page 110
110 Part 1 Introduction
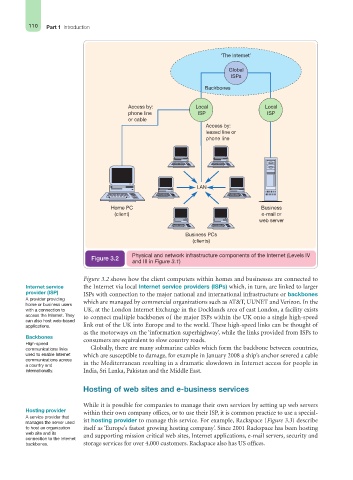
‘The Internet’
Global
ISPs
Backbones
Access by: Local Local
phone line ISP ISP
or cable
Access by:
leased line or
phone line
LAN
Home PC Business
(client) e-mail or
web server
Business PCs
(clients)
Physical and network infrastructure components of the Internet (Levels IV
Figure 3.2
and III in Figure 3.1)
Figure 3.2 shows how the client computers within homes and businesses are connected to
Internet service the Internet via local Internet service providers (ISPs) which, in turn, are linked to larger
provider (ISP) ISPs with connection to the major national and international infrastructure or backbones
A provider providing
home or business users which are managed by commercial organizations such as AT&T, UUNET and Verizon. In the
with a connection to UK, at the London Internet Exchange in the Docklands area of east London, a facility exists
access the Internet. They to connect multiple backbones of the major ISPs within the UK onto a single high-speed
can also host web-based
applications. link out of the UK into Europe and to the world. These high-speed links can be thought of
as the motorways on the ‘information superhighway’, while the links provided from ISPs to
Backbones
consumers are equivalent to slow country roads.
High-speed
communications links Globally, there are many submarine cables which form the backbone between countries,
used to enable Internet which are susceptible to damage, for example in January 2008 a ship’s anchor severed a cable
communications across
a country and in the Mediterranean resulting in a dramatic slowdown in Internet access for people in
internationally. India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan and the Middle East.
Hosting of web sites and e-business services
While it is possible for companies to manage their own services by setting up web servers
Hosting provider within their own company offices, or to use their ISP, it is common practice to use a special-
A service provider that
manages the server used ist hosting provider to manage this service. For example, Rackspace (Figure 3.3) describe
to host an organization itself as ‘Europe’s fastest growing hosting company’. Since 2001 Rackspace has been hosting
web site and its and supporting mission critical web sites, Internet applications, e-mail servers, security and
connection to the Internet
backbones. storage services for over 4,000 customers. Rackspace also has US offices.