Page 324 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 324
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 291
Chapter 5 E-business strategy 291
Box 5.5 Conversion modelling
A widely quoted conceptual measurement framework based on the industrial
marketing concepts of purchasing decision processes and hierarchy of effects models,
which can be applied for conversion marketing, was proposed by Berthon et al. (1998).
The model assesses efficiency of offline and online communications in drawing the
prospect through different stages of the buying decision. The main measures defined
in the model are the following ratios:
1 Awareness efficiency: target web-users/all web-users.
2 Locatability or attractability efficiency: number of individual visits/number of seekers.
3 Contact efficiency: number of active visitors/number of visits.
4 Conversion efficiency: number of purchases/number of active visits.
5 Retention efficiency: number of repurchases/number of purchases.
This model is instructive for improving Internet marketing within an organization since
these different types of conversion efficiency are key to understanding how effective
online and offline marketing communications are in achieving marketing outcomes.
So, to assess the potential impact of digital channels it is useful to put in place tracking or
research which assesses the cross-channel conversions at different stages in the buying
process. For example, phone numbers which are unique to the web site can be used as an
indication of the volume of callers to a contact centre influenced by the web site. This
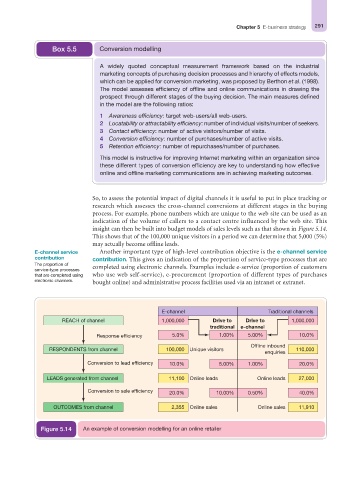
insight can then be built into budget models of sales levels such as that shown in Figure 5.14.
This shows that of the 100,000 unique visitors in a period we can determine that 5,000 (5%)
may actually become offline leads.
E-channel service Another important type of high-level contribution objective is the e-channel service
contribution contribution. This gives an indication of the proportion of service-type processes that are
The proportion of completed using electronic channels. Examples include e-service (proportion of customers
service-type processes
that are completed using who use web self-service), e-procurement (proportion of different types of purchases
electronic channels. bought online) and administrative process facilities used via an intranet or extranet.
E-channel Traditional channels
REACH of channel 1,000,000 Drive to Drive to 1,000,000
traditional e-channel
Response efficiency 5.0% 1.00% 5.00% 10.0%
Offline inbound
RESPONDENTS from channel 100,000 Unique visitors 110,000
enquiries
Conversion to lead efficiency 10.0% 5.00% 1.00% 20.0%
LEADS generated from channel 11,100 Online leads Online leads 27,000
Conversion to sale efficiency 20.0% 10.00% 0.50% 40.0%
OUTCOMES from channel 2,355 Online sales Online sales 11,910
Figure 5.14 An example of conversion modelling for an online retailer