Page 326 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 326
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 293
Chapter 5 E-business strategy 293
December, we want a confirmation from at least 80 per
cent of key customers that they consider the extranet to Questions
be a major reason to deal with Sandvik.’ 1 Summarize Sandvik Steel’s e-business strategy
By putting the internet at the heart of its business, the as described in the article.
Sandvik group intends to penetrate deeply into the minds 2 Suggest why the proportion of online purchases
and ambitions of its customers. ‘The challenge is not just varies in the different countries in which Sandvik
doing e-business, it is becoming an e-business’, she adds. trades.
Source: Andrew Fisher, Sandvik Steel, 4 June 2001
Activity 5.2 Assessing the significance of digital channels
Purpose
To illustrate the issues involved with assessing the suitability of the Internet for
e-commerce.
Activity
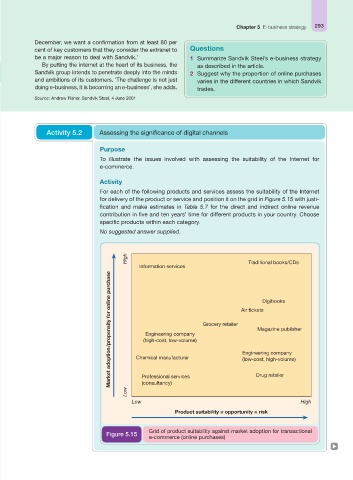
For each of the following products and services assess the suitability of the Internet
for delivery of the product or service and position it on the grid in Figure 5.15 with justi-
fication and make estimates in Table 5.7 for the direct and indirect online revenue
contribution in five and ten years’ time for different products in your country. Choose
specific products within each category.
No suggested answer supplied.
High Traditional books/CDs
Information services
purchase
online Digibooks
for Grocery retailer Air tickets
adoption/propensity Chemical manufacturer Engineering company
Magazine publisher
Engineering company
(high-cost, low-volume)
(low-cost, high-volume)
Market Professional services Drug retailer
(consultancy)
Low
Low High
Product suitability = opportunity = risk
Grid of product suitability against market adoption for transactional
Figure 5.15
e-commerce (online purchases)