Page 331 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 331
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 298
298 Part 2 Strategy and applications
Decision 1: E-business channel priorities
The e-business strategy must be directed according to the priority of different strategic
objectives such as those in Table 5.6. If the priorities are for the sell-side downstream channel,
as are objectives 1 to 3 in Table 5.6, then the strategy must be to direct resources at these
objectives. For a B2B company that is well known in its marketplace worldwide and cannot
offer products to new markets, an initial investment on buy-side channel upstream channel
e-commerce and value chain management may be more appropriate.
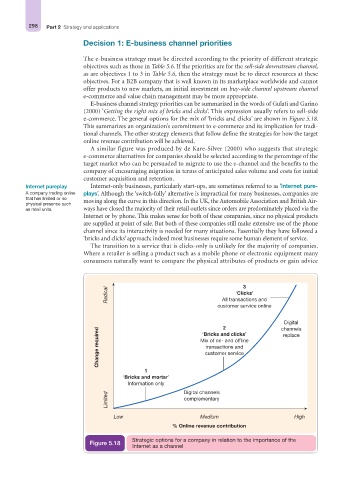
E-business channel strategy priorities can be summarized in the words of Gulati and Garino
(2000) ‘Getting the right mix of bricks and clicks’. This expression usually refers to sell-side
e-commerce. The general options for the mix of ‘bricks and clicks’ are shown in Figure 5.18.
This summarizes an organization’s commitment to e-commerce and its implication for tradi-
tional channels. The other strategy elements that follow define the strategies for how the target
online revenue contribution will be achieved.
A similar figure was produced by de Kare-Silver (2000) who suggests that strategic
e-commerce alternatives for companies should be selected according to the percentage of the
target market who can be persuaded to migrate to use the e-channel and the benefits to the
company of encouraging migration in terms of anticipated sales volume and costs for initial
customer acquisition and retention.
Internet pureplay Internet-only businesses, particularly start-ups, are sometimes referred to as ‘Internet pure-
A company trading online plays’. Although the ‘switch-fully’ alternative is impractical for many businesses, companies are
that has limited or no
physical presence such moving along the curve in this direction. In the UK, the Automobile Association and British Air-
as retail units. ways have closed the majority of their retail outlets since orders are predominately placed via the
Internet or by phone. This makes sense for both of these companies, since no physical products
are supplied at point of sale. But both of these companies still make extensive use of the phone
channel since its interactivity is needed for many situations. Essentially they have followed a
‘bricks and clicks’ approach; indeed most businesses require some human element of service.
The transition to a service that is clicks-only is unlikely for the majority of companies.
Where a retailer is selling a product such as a mobile phone or electronic equipment many
consumers naturally want to compare the physical attributes of products or gain advice
3
Radical All transactions and
ʻClicksʼ
customer service online
Digital
2
channels
required Mix of on- and offline replace
ʻBricks and clicksʼ
transactions and
Change customer service
1
ʻBricks and mortarʼ
Information only
Limited Digital channels
complementary
Low Medium High
% Online revenue contribution
Strategic options for a company in relation to the importance of the
Figure 5.18
Internet as a channel