Page 333 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 333
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 300
300 Part 2 Strategy and applications
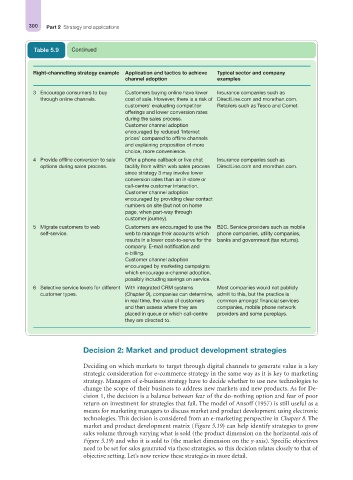
Table 5.9 Continued
Right-channelling strategy example Application and tactics to achieve Typical sector and company
channel adoption examples
3 Encourage consumers to buy Customers buying online have lower Insurance companies such as
through online channels. cost of sale. However, there is a risk of DirectLine.com and morethan.com.
customers’ evaluating competitor Retailers such as Tesco and Comet.
offerings and lower conversion rates
during the sales process.
Customer channel adoption
encouraged by reduced ‘Internet
prices’ compared to offline channels
and explaining proposition of more
choice, more convenience.
4 Provide offline conversion to sale Offer a phone callback or live chat Insurance companies such as
options during sales process. facility from within web sales process DirectLine.com and morethan.com.
since strategy 3 may involve lower
conversion rates than an in-store or
call-centre customer interaction.
Customer channel adoption
encouraged by providing clear contact
numbers on site (but not on home
page, when part-way through
customer journey).
5 Migrate customers to web Customers are encouraged to use the B2C. Service providers such as mobile
self-service. web to manage their accounts which phone companies, utility companies,
results in a lower cost-to-serve for the banks and government (tax returns).
company. E-mail notification and
e-billing.
Customer channel adoption
encouraged by marketing campaigns
which encourage e-channel adoption,
possibly including savings on service.
6 Selective service levels for different With integrated CRM systems Most companies would not publicly
customer types. (Chapter 9), companies can determine, admit to this, but the practice is
in real time, the value of customers common amongst financial services
and then assess where they are companies, mobile phone network
placed in queue or which call-centre providers and some pureplays.
they are directed to.
Decision 2: Market and product development strategies
Deciding on which markets to target through digital channels to generate value is a key
strategic consideration for e-commerce strategy in the same way as it is key to marketing
strategy. Managers of e-business strategy have to decide whether to use new technologies to
change the scope of their business to address new markets and new products. As for De-
cision 1, the decision is a balance between fear of the do-nothing option and fear of poor
return on investment for strategies that fail. The model of Ansoff (1957) is still useful as a
means for marketing managers to discuss market and product development using electronic
technologies. This decision is considered from an e-marketing perspective in Chapter 8. The
market and product development matrix (Figure 5.19) can help identify strategies to grow
sales volume through varying what is sold (the product dimension on the horizontal axis of
Figure 5.19) and who it is sold to (the market dimension on the y-axis). Specific objectives
need to be set for sales generated via these strategies, so this decision relates closely to that of
objective setting. Let’s now review these strategies in more detail.