Page 327 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 327
M05_CHAF9601_04_SE_C05.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:12 Page 294
294 Part 2 Strategy and applications
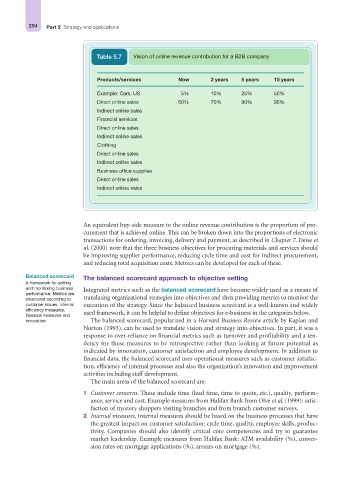
Table 5.7 Vision of online revenue contribution for a B2B company
Products/services Now 2 years 5 years 10 years
Example: Cars, US 5% 10% 25% 50%
Direct online sales 50% 70% 90% 95%
Indirect online sales
Financial services
Direct online sales
Indirect online sales
Clothing
Direct online sales
Indirect online sales
Business office supplies
Direct online sales
Indirect online sales
An equivalent buy-side measure to the online revenue contribution is the proportion of pro-
curement that is achieved online. This can be broken down into the proportions of electronic
transactions for ordering, invoicing, delivery and payment, as described in Chapter 7. Deise et
al. (2000) note that the three business objectives for procuring materials and services should
be improving supplier performance, reducing cycle time and cost for indirect procurement,
and reducing total acquisition costs. Metrics can be developed for each of these.
Balanced scorecard The balanced scorecard approach to objective setting
A framework for setting
and monitoring business Integrated metrics such as the balanced scorecard have become widely used as a means of
performance. Metrics are
structured according to translating organizational strategies into objectives and then providing metrics to monitor the
customer issues, internal execution of the strategy. Since the balanced business scorecard is a well-known and widely
efficiency measures,
financial measures and used framework, it can be helpful to define objectives for e-business in the categories below.
innovation. The balanced scorecard, popularized in a Harvard Business Review article by Kaplan and
Norton (1993), can be used to translate vision and strategy into objectives. In part, it was a
response to over-reliance on financial metrics such as turnover and profitability and a ten-
dency for these measures to be retrospective rather than looking at future potential as
indicated by innovation, customer satisfaction and employee development. In addition to
financial data, the balanced scorecard uses operational measures such as customer satisfac-
tion, efficiency of internal processes and also the organization’s innovation and improvement
activities including staff development.
The main areas of the balanced scorecard are:
1 Customer concerns. These include time (lead time, time to quote, etc.), quality, perform-
ance, service and cost. Example measures from Halifax Bank from Olve et al. (1999): satis-
faction of mystery shoppers visiting branches and from branch customer surveys.
2 Internal measures. Internal measures should be based on the business processes that have
the greatest impact on customer satisfaction: cycle time, quality, employee skills, produc-
tivity. Companies should also identify critical core competencies and try to guarantee
market leadership. Example measures from Halifax Bank: ATM availability (%), conver-
sion rates on mortgage applications (%), arrears on mortgage (%).